Fig. 4.
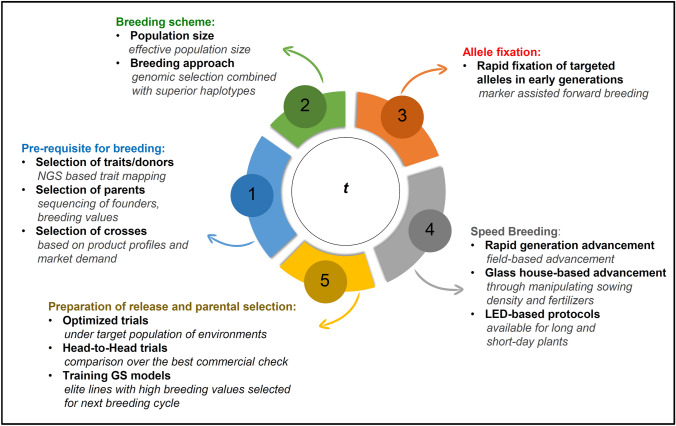
Accelerating the breeding cycle time (t). The breeding cycle starts with the selection of traits/donors/parents for the crossing programs based on the market demands which can be selected through precise phenotyping and WGRS for identification of appropriate genes/alleles/haplotypes. A genomic selection-based approach with appropriate population size can be adopted to develop lines with higher genetic gain. Lines can be fixed quickly through rapid fixation of alleles through forward breeding approach. Speed breeding/rapid generation advancement (RGA) approaches can be utilized for the advancing generations in fields or under controlled conditions. The preparation of lines for commercial release is an important step in which phenotypic evaluation of lines under target population of environments (TPEs) is a crucial step together with head-to-head trials of newly developed lines with local and national checks. Data generated through these trials can be utilized in selection of elite parental lines and can inform genomic selection cycle. Genetic gain per unit time can be improved through incorporating the above-discussed points which shall be useful in shortened cycle time (t) by integrated breeding strategies