Fig. 9.
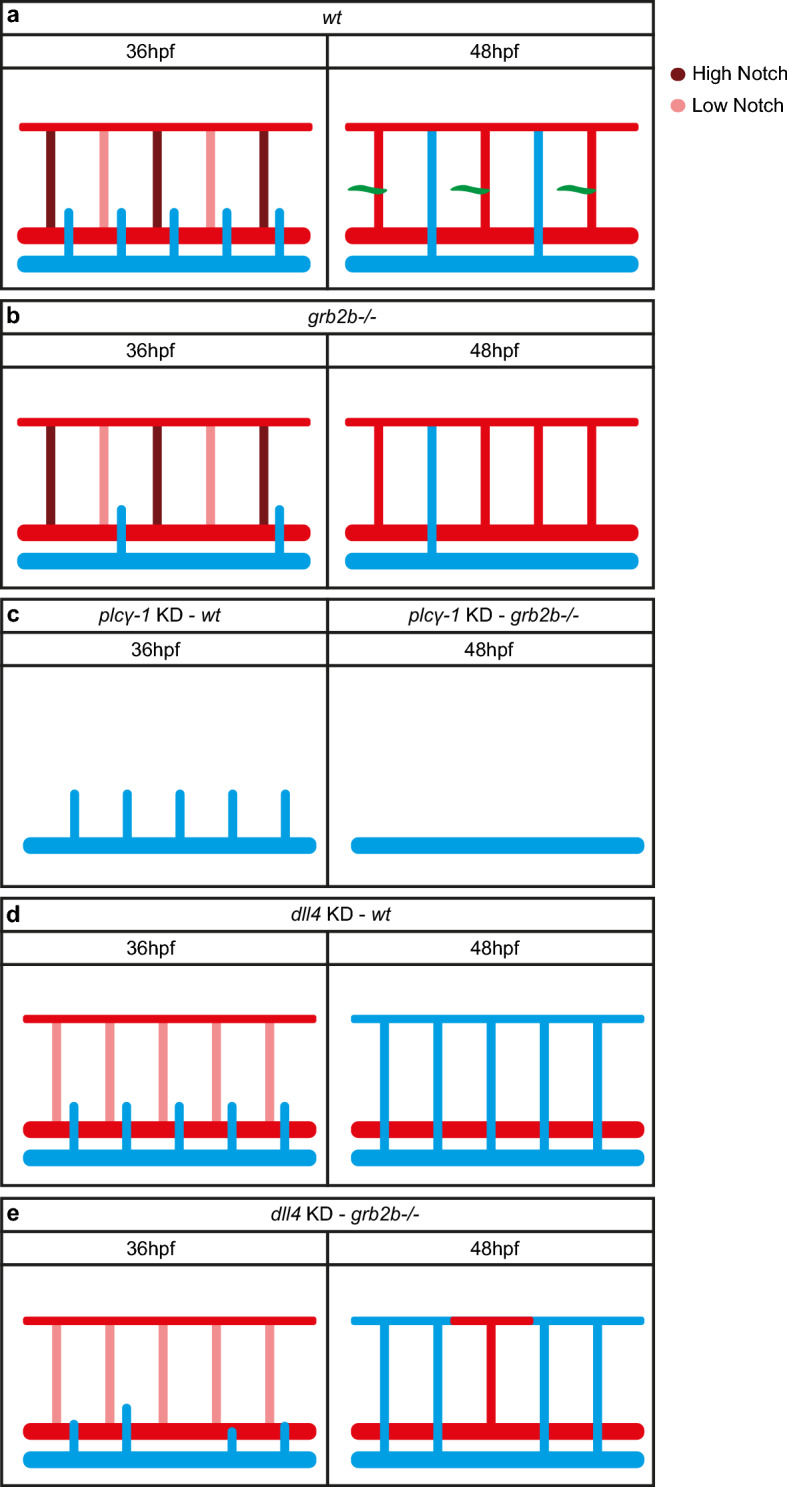
grb2b is essential for cells to sprout from the PCV and for PL formation, but not for vein formation. a In wild-type embryos, secondary sprouts are either forming PLs, shown in green (if they are close to an aISV with high Notch signaling levels), or a vISV (in case the aISV has low levels of Notch activity). b grb2b mutant embryos show defective secondary sprouting. If a cell protruding from the PCV encounters an intersegmental artery with high Notch levels, then it will retract towards the PCV, not being able to migrate to the HM. If the cell makes contact with a low Notch signaling artery, it will form an intersegmental vein. c Upon plcγ-1 knockdown, no intersegmental arteries develop. In wild-type embryos sprouts normally migrate out from the PCV, whereas no stable sprout is detected at 48hpf in grb2b mutants. d, e Upon dll4 knockdown most of aISVs are remodeled into vISVs in both wild-type and grb2b mutant embryos, indicating that a connection between a cell in the PCV and the intersegmental artery is sufficient for a venous endothelial cell to form a vein
