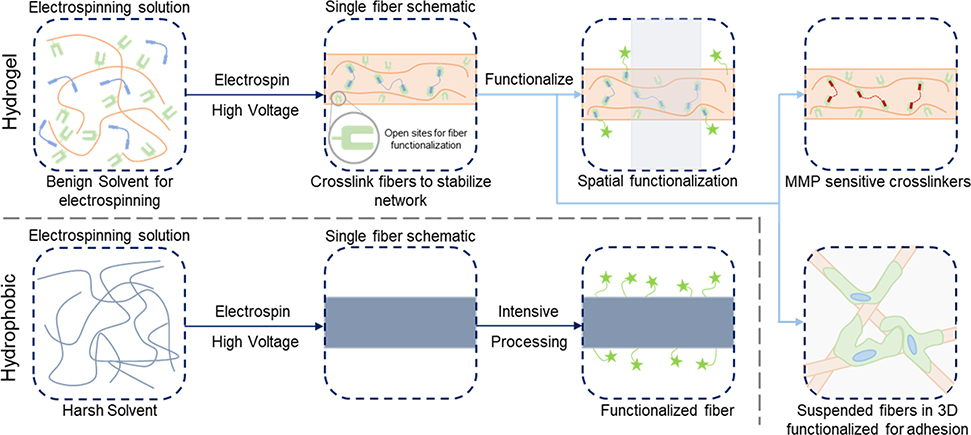
Figure 1. Functionalization of hydrogel versus hydrophobic nanofibers.
(Top, left to right): electrospinning precursor solution containing a hydrophilic polymer with a crosslinker to stabilize hydrogel nanofibers; solution is electrospun and crosslinked (e.g. with UV irradiation) with leftover sites for further functionalization; three example pathways to functionalize the fibers – spatial control over bioactivity (green stars, shaded area indicates unfunctionalized region)86, fibers crosslinked with matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) sensitive crosslinkers for tunable degradation8, suspended hydrogel fibers in a bulk gel for 3D models of the ECM123. (Bottom, left to right): electrospinning precursor solution containing hydrophobic polymer (typically in a harsh solvent); solution is electrospun and fibers are ready for processing; intensive chemical processing is typically needed for fiber functionalization.