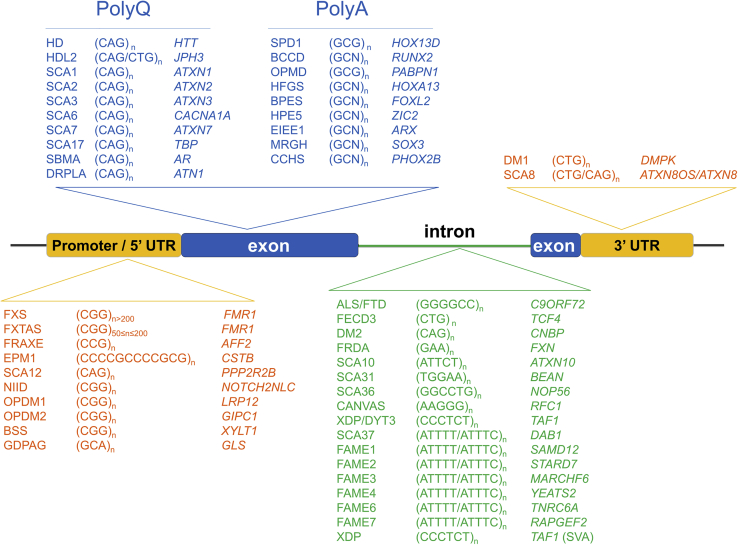
Figure 2.
Location of repeat expansions within genes
Repeat expansions may affect coding regions (mainly encoding polyglutamine or polyalanine tracts) or noncoding regions of genes. Noncoding repeat expansions are mainly located in promoters or 5′ untranslated regions (UTRs) or introns. Noncoding repeats in 5′ regions are often GC-rich and their expansion usually affects gene expression through methylation of other epigenetic processes. Intronic expansions and expansions affecting 3′ UTRs more often lead to RNA toxicity or polypeptide synthesis via repeat-associated non-AUG (RAN) translation and subsequent formation of cellular/nuclear aggregates. BCCD, brachydactyly and cleidocranial dysplasia; BSS, Baratela-Scott syndrome; CANVAS, cerebellar ataxia, neuropathy and vestibular areflexia syndrome; CCHS, congenital central hypoventilation syndrome; DM1, myotonic dystrophy type 1; DM2, myotonic dystrophy type 2; DRPLA, dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy; EIEE1, early infantile epileptic encephalopathy type 1; EPM1, progressive myoclonus epilepsy type 1 (Unverricht-Lundborg disease); FAME, familial adult myoclonic epilepsy; FECD3, Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy type 3; FRAXE, fragile XE syndrome; FRDA, Friedreich ataxia; FTD/ALS, frontotemporal dementia / amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; FXS, fragile X syndrome; FXTAS, fragile X-associated tremor ataxia syndrome; GDPAG, global developmental delay, progressive ataxia, and elevated glutamine; HD, Huntington disease; HDL2, Huntington disease-like 2; HFGS, hand-foot-genital syndrome; HPE5, holoprosencephaly type 5; MRGH, mental retardation with isolated growth hormone deficiency; OPMD, oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy; NIID, neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease; OPDM1, oculopharyngodistal myopathy type 1; OPDM2, oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy type 2; OPML1, oculopharyngeal myopathy with leukoencephalopathy type 1; SBMA, spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy; SPD1, synpolydactyly type 1; SCA, spinocerebellar ataxia; SVA, SINE-VNTR-Alu retrotransposon; XDP, X-linked dystonia parkinsonism.