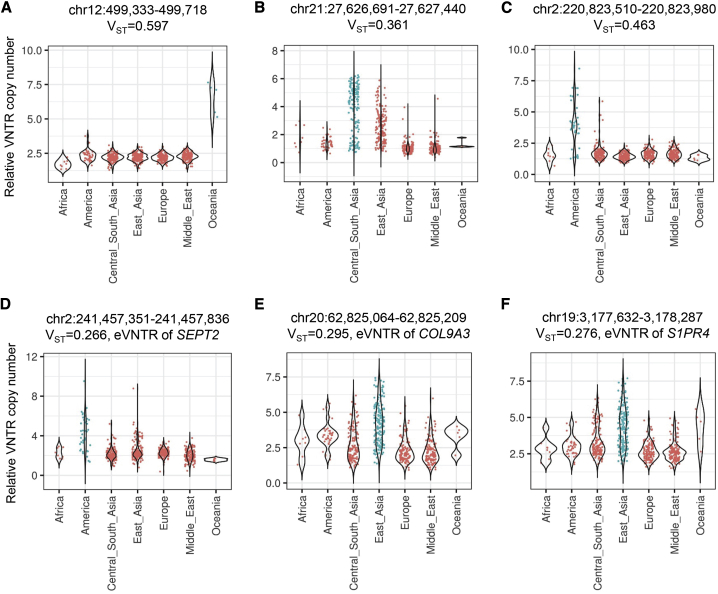
Figure 6.
VNTRs with high population divergence are enriched for functional associations with gene expression, methylation, and human traits
We estimated population stratification of VNTR copy number with the VST statistic in samples from the Human Genome Diversity Panel. Both eVNTRs and mVNTRs were enriched for VNTRs with high VST, and consistent with the notion that selection may have acted to modify copy number of functional VNTR loci in specific populations, we also observed that eVNTRs with elevated VST were enriched for putative phenotype associations. Shown are six example VNTRs with high VST.
(A) A 40-mer VNTR (chr12: 499,333–499,718, hg38) expanded in the Oceanic population.
(B) A 33-mer VNTR (chr21: 27,626,691–27,627,440, hg38) expanded in Asians.
(C) A 20-mer VNTR (chr2: 220,823,510–220,823,980, hg38) expanded in Americans.
(D) An 81-mer VNTR (chr2: 241,457,351–241,457,836, hg38) expanded in Americans is associated with expression level of SEPT2 (MIM: 601506) in skin and thyroid and is potentially linked to multiple human traits by GWASs.
(E) A 24-mer VNTR (chr20: 62,825,064–62,825,209, hg38) expanded in East Asians is associated with expression level of COL9A3 (MIM: 120270) in adipose tissue, muscle, and blood.
(F) A 39-mer VNTR (chr19: 3,177,632–3,178,287, hg38) expanded in East Asians is associated with expression level of S1PR4 (MIM: 603751) in mammary tissue, thyroid, and esophagus.