FIGURE 1.
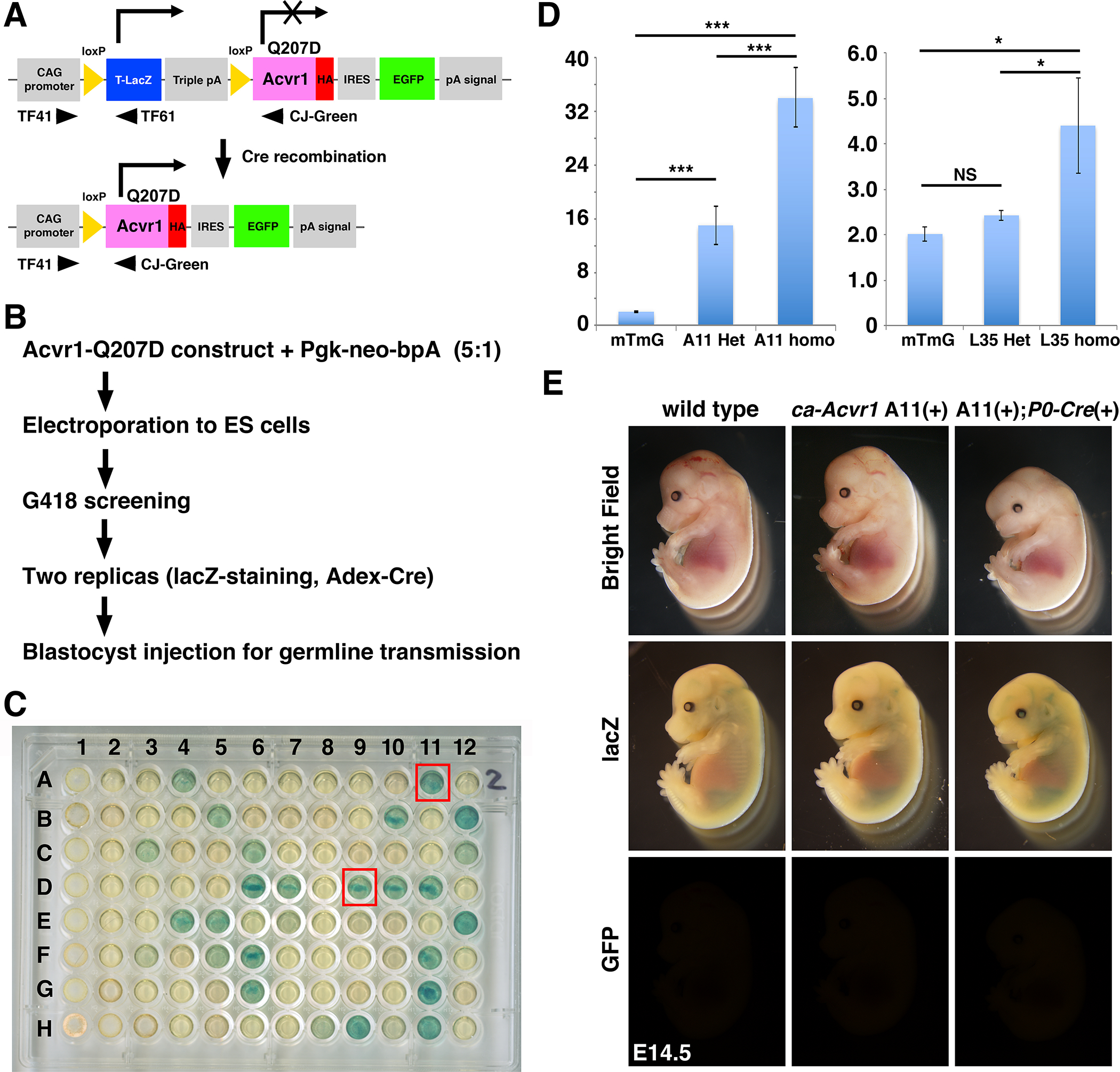
Generation of constitutively activated ACVR1 mouse line and initial characterization. A: A concept of the transgenic construct. Human ACVR1 cDNA with the Q207D mutation was ligated with IRES-EGFP and also ligated with the CAG promoter but intercepted by a floxed lacZ cassette with triple polyA sites. Cells with this transgenic construct are expected to generate beta-galactosidase from the lacZ cassette. Cre-dependent DNA recombination removed triple polyA sites to generate ACVR1 with Q207D protein (constitutively activated ACVR1, ca-ACVR1) and to produce GFP fluorescence. Approximate positions of three PCR primers for genotyping are shown. Sequence information of those primers are shown in Supplemental Table 1. B: Screening strategy. The linearized transgenic construct was electroporated into ES cells with a Pgk-neo selection vector. Ninety eight G418-resistance clones were picked up and examined their beta-galactosidase activity and capability to recombination capability by Cre. C: lacZ staining results. Replicated cells were stained with X-gal. Two clones that showed strong signal, A11 and D9, were further propagated and injected to blastocysts for germline transmission. D: Quantitative genomic PCR for copy number estimation. Homozygous mice for mTmG are used as a control (1 copy of EGFP per haploid). n=3. Sequence information of TaqMan primers are shown in Supplementary Table 2. E: Initial characterization of ca-Acvr1 line A11. After breeding with P0-Cre mice, embryos were harvested at E14.5. After observation of EGFP, embryos were stained with X-gal. Littermates who did not have both transgenes were used as wild type.
