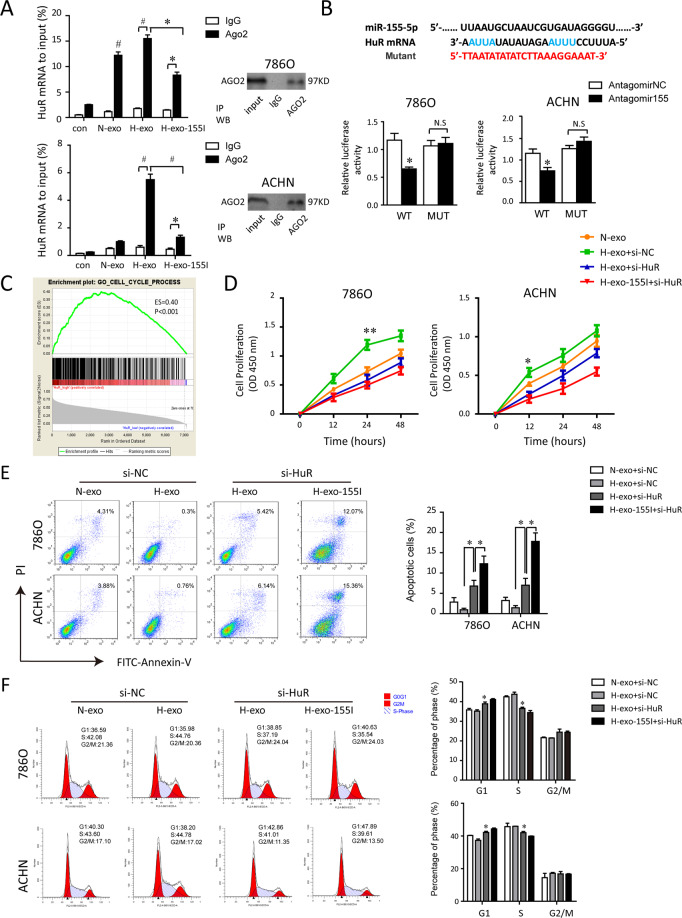
Fig. 5. Exosomal miR-155-5p contributes to the malignant phenotypes of RCC cells by binding to HuR.
A HuR mRNA was associated with amount of exosomal miR-155-5p in Ago2. RNA immunoprecipitation with an anti-Ago2 antibody assessed endogenous Ago2 binding to RNA in RCC cells treated with blank, N-exo, H-exo, H-155I-exo, respectively. IgG served as the negative control. RIP efficiency of Ago2 protein was detected by western blot. The relative HuR mRNA levels were determined by qRT–PCR and presented as fold enrichment in Ago2 relative to input. B HuR is a direct target of miR-155-5p. Dual-luciferase reporter assays were conducted to confirm a direct interaction between miR-155-5p and HuR in 786-0 and ACHN cells. Upper panel, sequence alignment of miR-155-5p and its putative-binding sites in HuR mRNA 3′-UTR containing an ARE motifs (AUUA, AUUU). Predicted miR-155-5p target region in HuR (Luc-WT) and mutant type (Luc-MUT) were constructed and transfected into RCC cells with antagomiR-155-5p or control. Luciferase activity is presented as relative luciferase activity normalized to activity of their respective negative control. C Results of gene-set enrichment analysis (GSEA) were plotted to visualize the correlation between the expression of HuR and cell cycle gene signatures in TCGA cohort. D CCK-8 assays demonstrated HuR silencing inhibited RCC cell growth. E, F The effect of HuR knockdown on cell apoptosis and cell cycle were analyzed by flow cytometry. The experiment was performed in triplicate. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, #P < 0.01.