Figure 4.
Classification of samples using SVM machine learning models based on each DNAm signature
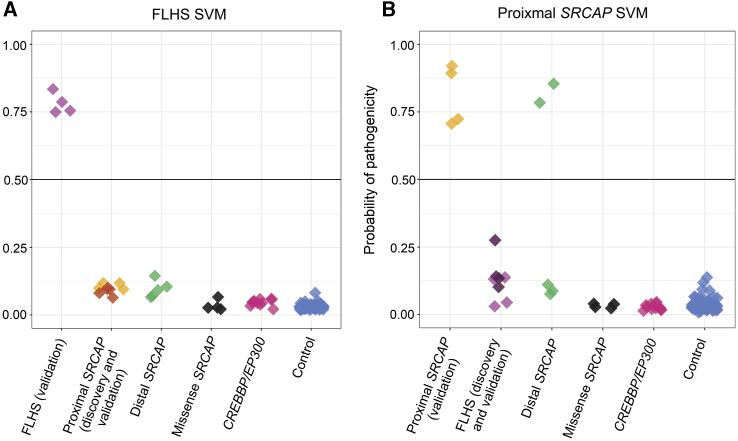
Sample groups were scored using (A) the FLHS support vector machine (SVM) model and (B) the proximal SRCAP SVM model. FLHS validation subjects (n = 4) classified positively using the FLHS model; similarly proximal SRCAP validation subjects (n = 4) classified positively using the proximal SRCAP model, demonstrating 100% sensitivity of both models. Using the FLHS model, proximal SRCAP subjects (n = 9) and validation control subjects (n = 97) classified negatively, demonstrating 100% specificity of the model. Using the proximal model, FLHS subjects (n = 8) and validation control subjects (n = 97) classified negatively demonstrating 100% specificity of the model. SRCAP missense variants (n = 4) classified negatively using both models, suggesting them to be benign. Distal SRCAP subjects (n = 5) all classified negatively on the FLHS signature, suggesting these subjects do not have FLHS. Two distal SRCAP subjects classified positively on the proximal SRCAP model (distal SRCAP individual #1 and #2) demonstrating concordant DNAm profiles of these subjects with the proximal SRCAP subjects, while three classified negatively (distal SRCAP individual #3, #4, and #5). Subjects with a pathogenic variant in CREBBP (n = 10) or EP300 (n = 1) all classified negatively using both models.