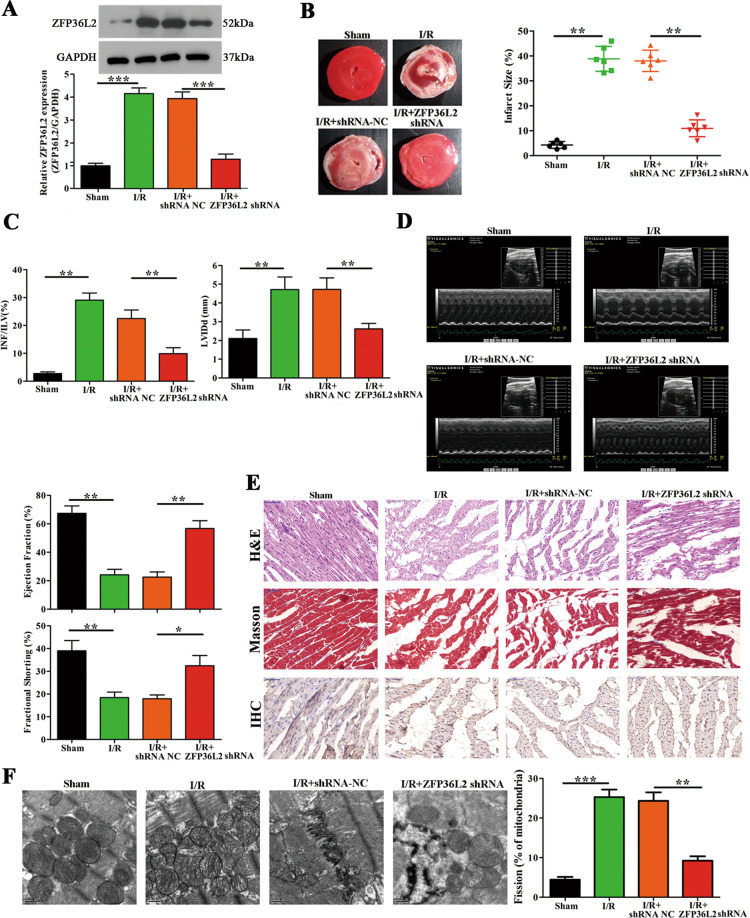
Fig. 1. ZFP36L2 knockdown inhibites myocardial I/R injury and attenuates mitochondrial fusion and fission in vivo.
A A myocardial I/R injury model was established by inducing ischemia for 45 min following 4 h of reperfusion (n = 6 per group). ZFP36L2 shRNA and shRNA-NC were intraperitoneally administered 24 h before induction of I/R injury. RNA was isolated from cardiomyocytes and mRNA and protein levels of ZFP36L2 were determined by qRT-PCR and western blot (n = 6). B The left panel shows representative images of tissue samples. The right panel indicates infarction size (%) (n = 6). C Quantification of the extent of injury measured by infarction area/left ventricle (INF/LV) and diastolic diameter of the left ventricle (LVIDd) (n = 6). D Representative echocardiograms at 4 h post I/R injury. The percentage of ejection fraction (EF) and fractional shorting (FS) were shown (n = 6). E Representative images of H&E and Masson’s trichrome staining and immunohistochemistry staining for ZFP36L2 in LV sections (Scale bar = 50 μm) (n = 6). F Representative TEM images of heart tissues shown in the left panel and the corresponding quantification of fragmented mitochondria shown in the right panel (Scale bar = 0.5 μm) (n = 6). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.