Figure 2.
In silico protein modeling of SIN3B nonsynonymous variants indicate likely disruption of protein function
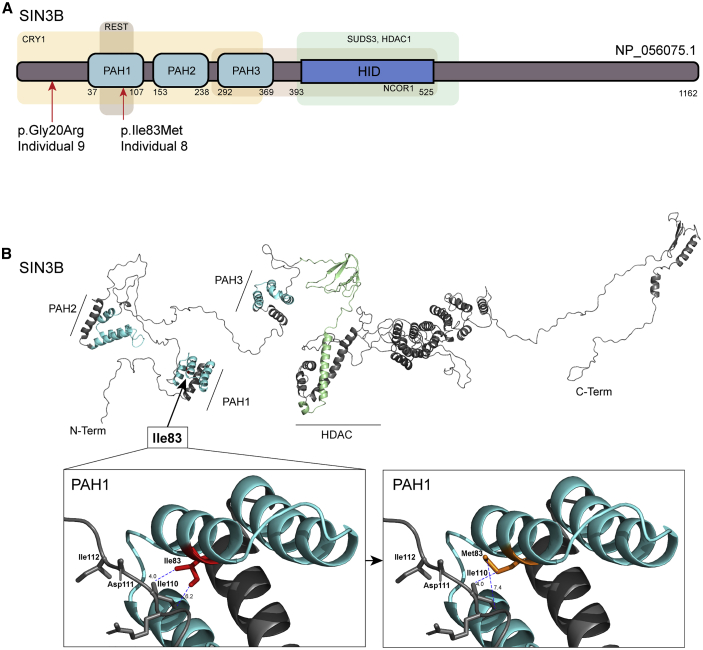
(A) SIN3B protein structure (GenBank: NP_056075.1). Three paired amphipathic helix (PAH domains) predicted on the N-terminal region of SIN3B are indicated by light blue boxes. Regions that interact (predicted by similarity with murine Sin3b) with CRY1 (cryptochrome circadian clock 1), REST (RE1-silencing transcription factor), SUDS (Sin3 histone deacetylase corepressor complex component SDS), HDAC1 (histone deacetylase 1), NCOR1 (nuclear receptor corepressor 1), and HID (HDAC-interacting domain) are indicated by light-colored boxes.
(B) In silico three-dimensional view of SIN3B. Variant c.249C>G encodes p.Ile83Met, which affects a residue located in the PAH1 domain nearest to the N terminus, which is predicted to mediate protein-protein interaction with transcriptional corepressors REST and CRY1. Protein Data Bank (PDB) file was generated by RaptorX and analyzed in Pymol 2.0. PAH domains are colored in turquoise and HID is colored in light green. Distance (Å) between side chains of wild-type (Ile83; left box) and mutant (Met83; right box) SIN3B and the closest residue on the opposing side of the protein are measured as indicated (blue dashed lines).