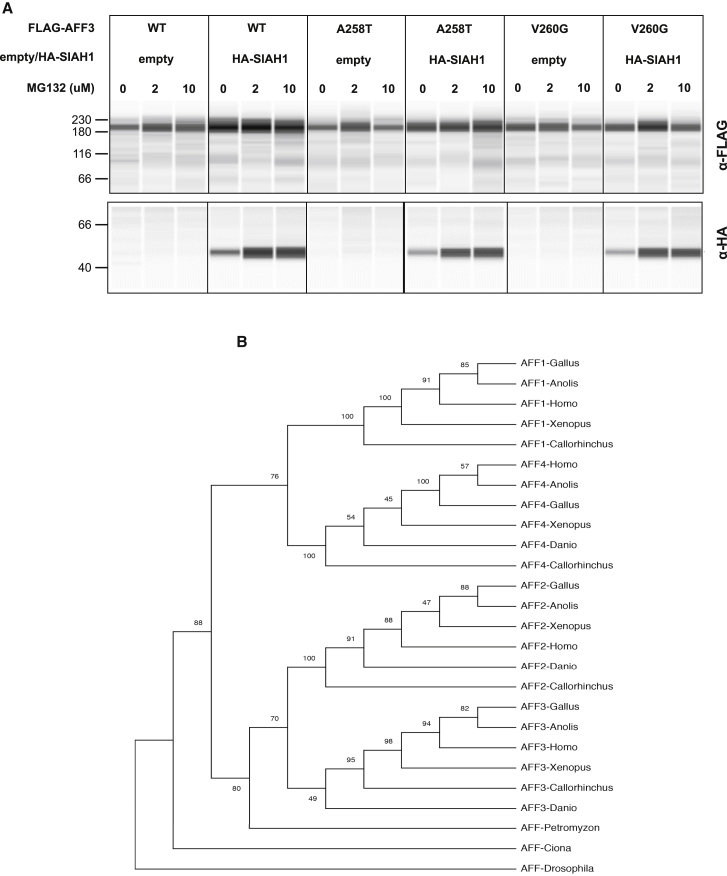
Figure 2.
AFF3 stability and evolution
(A) Immunoassays comparing the stability of wild-type and mutated forms of AFF3 proteins. We transiently co-transfected HEK293T cells with expression vectors encoding FLAG-tagged AFF3wild-type (WT), AFF3A258T (A258T), or AFF3V260G (V260G) proteins and HA-tagged SIAH1 E3-ligase (HA-SIAH1) or an empty vector (empty) in presence/absence of increasing amount of the MG132 proteasome inhibitor (0, 2, and 10 μM). Protein extracts were separated by capillarity on a Jess system and immunoassayed with an anti-FLAG antibody (upper portion) and an anti-HA antibody (bottom portion). The image shows a typical example of eight replicas performed in the same conditions. Loading control and normalization are shown in Figure S1.
(B) ALF protein phylogeny. The maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree was constructed with 26 AFF amino acid sequences: mammals: Homo sapiens AFF1 (NP_001160165.1), AFF2 (NP_002016.2), AFF3 (NP_002276.2), and AFF4 (NP_055238.1); birds: Gallus gallus AFF1 (XP_004941155.1), AFF2 (XP_015134139.2), AFF3 (XP_015133277.1), and AFF4 (XP_015149549.1); reptiles: Anolis carolinensis AFF1 (XP_008109400.2), AFF2 (XP_016851830.1), AFF3 (XP_008118477.1), and AFF4 (XP_003217431.2); amphibians: Xenopus laevis AFF1 (XP_018108715.1), AFF2 (XP_018088502.1), AFF3 (XP_018104097.1), and AFF4 (XP_018107624.1); bony fishes: Danio rerio AFF2 (XP_002664429.2), AFF3 (XP_021334573.1), and AFF4 (XP_005173956.1); cartilaginous fishes: Callorhinchus milii AFF1 (XP_007895125.1), AFF2 (XP_007891068.1), AFF3 (XP_007884050.1), and AFF4 (XP_007889648.1); lamprey: Petromyzon marinus AFF (PMZ_0026877); tunicate: Ciona intestinalis AFF (XP_018673247.1); and invertebrates: Drosophila melanogaster AFF (NP_722863.1). The bootstrap consensus tree inferred from 100 replicates is shown.