Figure 1.
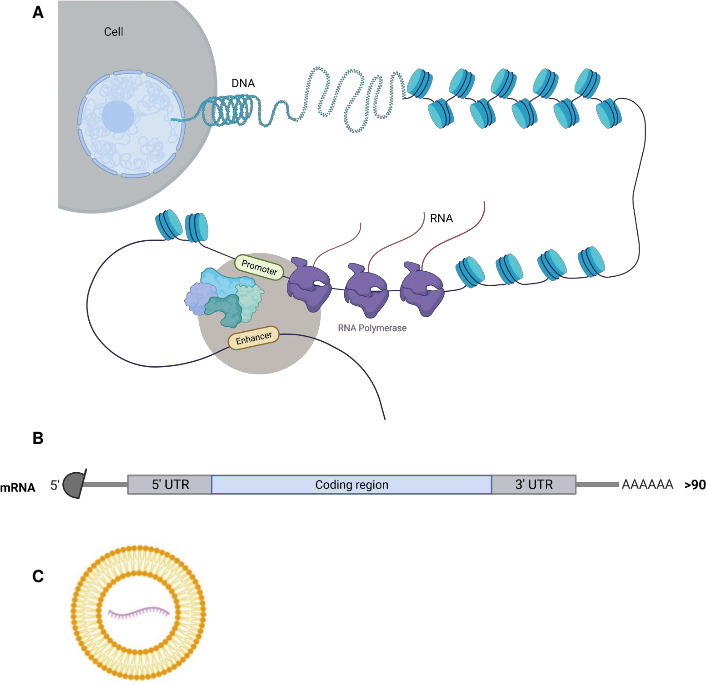
In vitro transcribed (IVT) mRNA-based vaccines. (A) The DNA in the nucleus is transcribed into mRNA by RNA polymerases. The same process is used for in vitro production of mRNA. The recognition of a specific promoter allows the transcription of the desired synthetic mRNA in vitro. (B) The mRNA structure (natural and synthetic) of eukaryotes consists of a 5′ Cap structure (7-methylguanosine linked from its 3′ with a triphosphate bond to the 5′ of the first nucleotide), a 5′ untranslated region (5′ UTR), the coding sequence starting with AUG and ending on a stop codon, and a 3′ UTR followed by a poly-A tail of usually more than 90 residues. (C) The SARS-CoV-2 IVT mRNA-based vaccines from Moderna and BioNTEch/Pfizer use a liposome-based delivery vehicle. (Note: This figure was generated using images from BioRender.)
