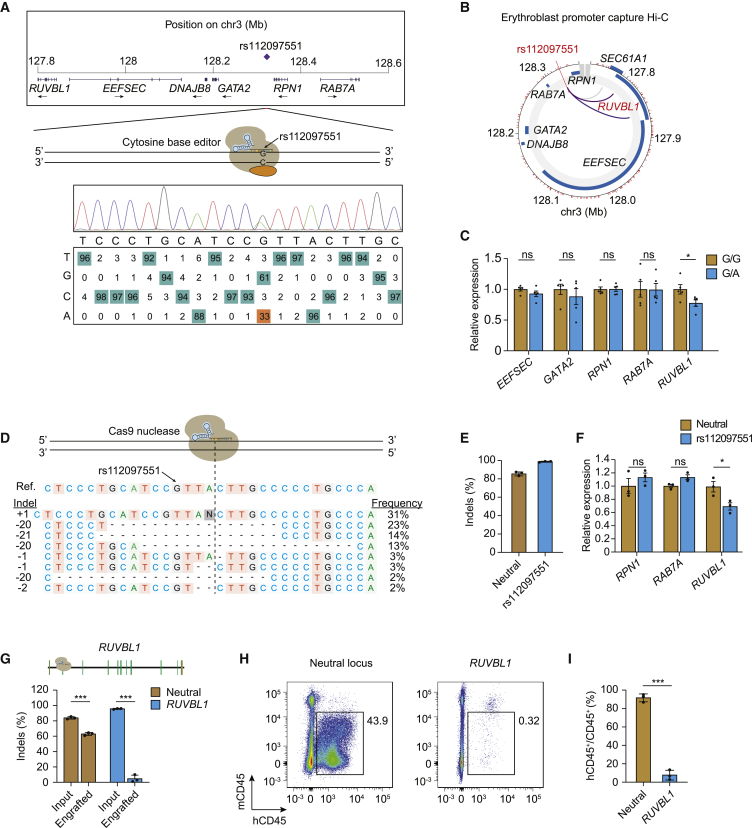
Figure 1.
Gene editing implicates RUVBL1 in rs112097551 association
(A) The MCV/MCH-associated variant rs112097551 was targeted by cytosine base editing in HUDEP-2 cells expressing AncBE4max-SpRY and sgRNA to convert G-to-A. Sequencing chromatogram and heatmap of bulk edited HUDEP-2 cells generated by EditR analysis.
(B) Promoter capture Hi-C from ChiCP analysis49 of erythroblasts.50
(C) Gene expression measured by RT-qPCR in rs112097551-G/G (n = 5) and -G/A (n = 5) HUDEP-2 base edited clones. Expression normalized to mean of G/G clones for each gene.
(D) Representative allele table demonstrating type and frequency of indels following nuclease editing in CD34+ HSPCs following 3xNLS-SpCas9:sgRNA electroporation. Indels analyzed by TIDE analysis.45
(E) Indel frequency measured by Sanger sequencing with TIDE analysis in CD34+ HSPCs 4 days following 3xNLS-SpCas9:sgRNA electroporation with indicated sgRNA (n = 3 biological replicates).
(F) Gene expression measured by RT-qPCR in CD34+ HSPCs 4 days following 3xNLS-SpCas9:sgRNA targeting adjacent to rs112097551 compared to neutral locus. Expression of EEFSEC and GATA2 was undetectable in HSPCs.
(G) Indel frequency following 3xNLS-SpCas9:sgRNA targeting RUVBL1 coding sequence or neutral control locus in input cell 4 days after RNP electroporation or engrafted bone marrow samples 16 weeks after infusion to NBSGW mice.
(H) Representative flow cytometry of human and mouse CD45+ cells from NBSGW bone marrow 16 weeks after cell infusion (representative of 3 mice).
(I) Mean human hematopoietic chimerism determined by hCD45+/total CD45+ cells from NBSGW bone marrow 16 weeks after cell infusion (n = 3 mice per group).
Student’s t test (two-tailed test). ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗p < 0.05; ns, not significant. All error bars indicate mean and standard deviation.