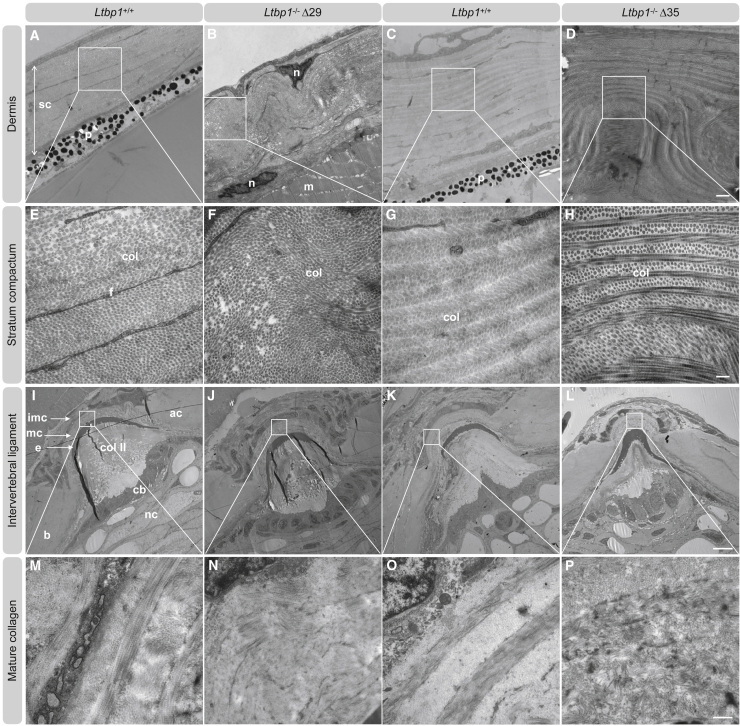
Figure 7.
LTBP1 deficiency causes abnormal collagen fibrillogenesis in skin and intervertebral ligaments
(A–H) Representative images of ultrathin sections taken from the dermis of 4-months old adult ltbp1−/− Δ29 zebrafish, ltbp1−/− Δ35 zebrafish, and corresponding WT siblings. Increased interfibrillar spaces and disorganized collagen architecture are noted in ltbp1−/−Δ29 and ltbp1−/−Δ35 zebrafish samples. Col, collagen; f, fibroblast; m, muscle; n, nucleus; p, pigmentation; sc, stratum compactum. Scale represents 1 μm in (A)–(D) and scale represents 200 nm in (E)–(H).
(I–P) Representative images of ultrathin parasagittal sections showing internal structures of zebrafish vertebral centra and intervertebral ligament of 4-months-old adult ltbp1−/−Δ29 and ltbp1−/−Δ35 zebrafish and corresponding WT siblings. Note that the notochord sheet is composed of collagen type II. Collagen type II is secreted by the chordoblasts lining the notochord sheet on the inside and in between the chordocytes and the notochord sheet. Abnormal mature collagen architecture is noted in adult ltbp1−/−Δ29 and ltbp1−/−Δ35 zebrafish compared to corresponding WT siblings. Ac, autocenter; b, bone; cb, chordoblasts; colII, collagen type II (notochord sheet); e, outer elastin layer; imc, immature collagen; mc, mature collagen; nc, vacuolated notochord cells (chordocytes). Scale represents 200 μm in (I)–(L) and scale represents 500 nm in (M)–(P).