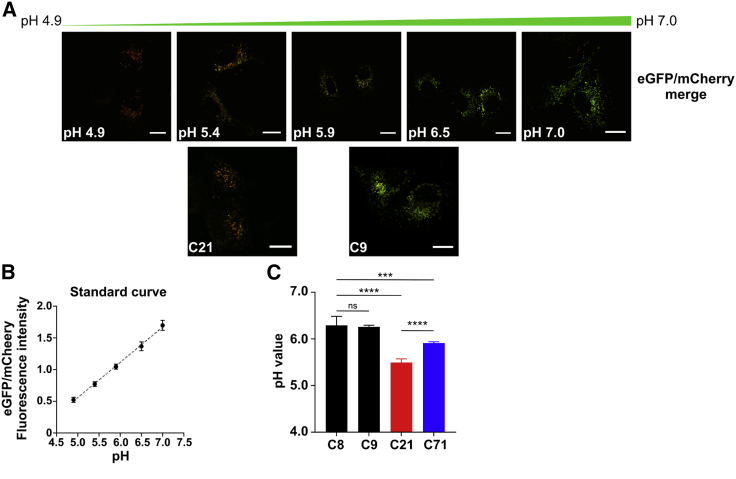
Figure 6.
Calibration and quantification of the Golgi pH in Huh7 control and edited cells
(A) Calibration buffers were used to create a pH response curve for the GalT-mCherry-eGFP construct and allowed for the calculation of pH in Huh7 cells. Scale bar represents 20 µm.
(B) Standard curve using calibration buffers to determine estimated luminal pH values.
(C) Quantification of the Golgi luminal pH values in Huh7 controls (C8 and C9) and edited (C21, a homozygous clone, and C71, a heterozygous clone) cells showing acidification of the Golgi upon introduction of the c.1267C>T (p.Arg423∗) mutation. The effect is significantly more pronounced when both alleles are mutated. Data were acquired in four (C8 and C71) or six (C9 and C21) biological replicates, conducted on different weeks, with cells freshly transfected with GalT-mCherry-eGFP construct. In each biological replicate, 10–15 cells were analyzed, and the mean was taken. The graph represents an average of the means acquired over the different biological measurements. Statistical significance ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.005, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 was calculated via one-way ANOVA.