Figure 2.
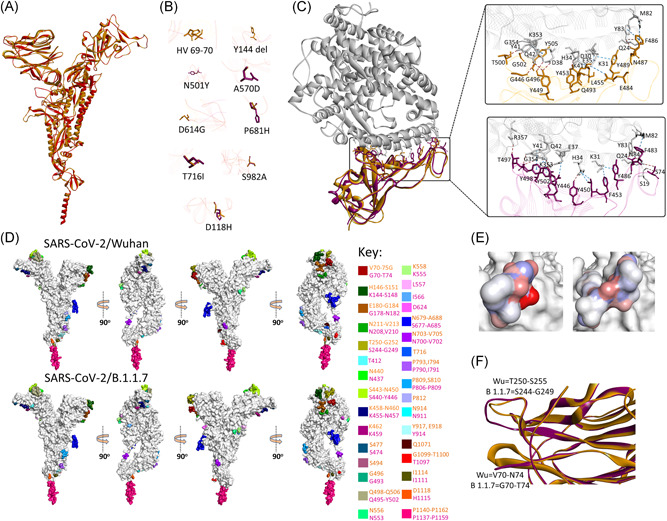
Structure and epitopes of SARS‐CoV‐2/B.1.1.7 spike protein. (A) Structural comparison in ribbon conformation of spike proteins of SARS‐CoV‐2/Wuhan (gold) and SARS‐CoV‐2/B.1.1.7 (magenta). (B) Stick representation of the spatial orientation of amino acids of SARS‐CoV‐2/Wuhan spike protein (gold) compared with substituting amino acids in SARS‐CoV‐2/B.1.1.7 spike protein (magenta). (C) Comparison of the intermolecular interactions between ACE2 receptor (gray ribbon) and RBD domain of SARS‐CoV‐2/Wuhan spike (gold ribbon) and SARS‐CoV‐2/B.1.1.7 spike (magenta ribbon). Intermolecular hydrogen bonds and non‐hydrogen bond intermolecular interactions (electrostatic and hydrophobic) are shown with brown and blue‐dotted lines, respectively, in the enlarged views. (D) Surface topology view with 360° rotation of epitope distribution in the spike proteins of SARS‐CoV‐2/Wuhan and SARS‐CoV‐2/B.1.1.7, as labeled. Corresponding epitopes in terms of position within spike protein are colored differently as mentioned in key. (E) Electrostatic surface of the corresponding epitope found variable between SARS‐CoV‐2/Wuhan (left) and SARS‐CoV‐2/B.1.1.7 spike proteins (right). (F) Structural variation in the loops between β3 and β4 (bottom) and β14 and β15 (top) are shown in ribbon conformation, where spike protein of SARS‐CoV‐2/Wuhan and SARS‐CoV‐2/B.1.1.7 are shown with gold and magenta colors, respectively
