Figure 4.
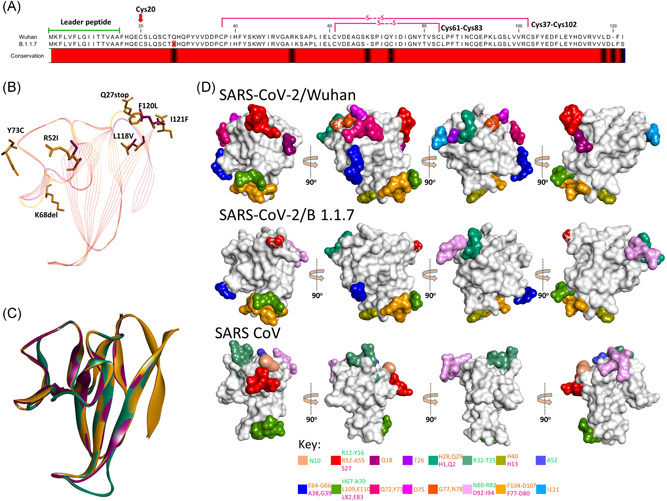
Comparison of SARS‐CoV‐2/Wuhan and SARS‐CoV‐2/B.1.1.7 orf8. (A) Sequence alignment of orf8 of SARS‐CoV‐2/Wuhan and SARS‐CoV‐2/B.1.1.7 showing leader peptide region and cysteine involved in intramolecular disulfide bonds. Note the presence of the stop codon at position 27 in SARS‐CoV‐2/B.1.1.7. The variable amino acids are indicated by the black color in the conservation bar. (B) Stick representation of the spatial orientation of amino acids of SARS‐CoV‐2/Wuhan orf8 (gold) compared with substituting amino acids in SARS‐CoV‐2/B.1.1.7 orf8 (magenta). (C) Structural comparison of orf8 in ribbon conformation of SARS‐CoV (green), SARS‐CoV‐2/Wuhan (gold), and SARS‐CoV‐2/B.1.1.7 (magenta). (D) Surface topology view with 360° rotation of epitope distribution in the orf8 of SARS‐CoV‐2/Wuhan and orf8b of SARS‐CoV and SARS‐CoV‐2/B.1.1.7, as labeled. Corresponding epitopes in terms of position within orf8/8b are colored differently (key given at the bottom)
