Figure 4.
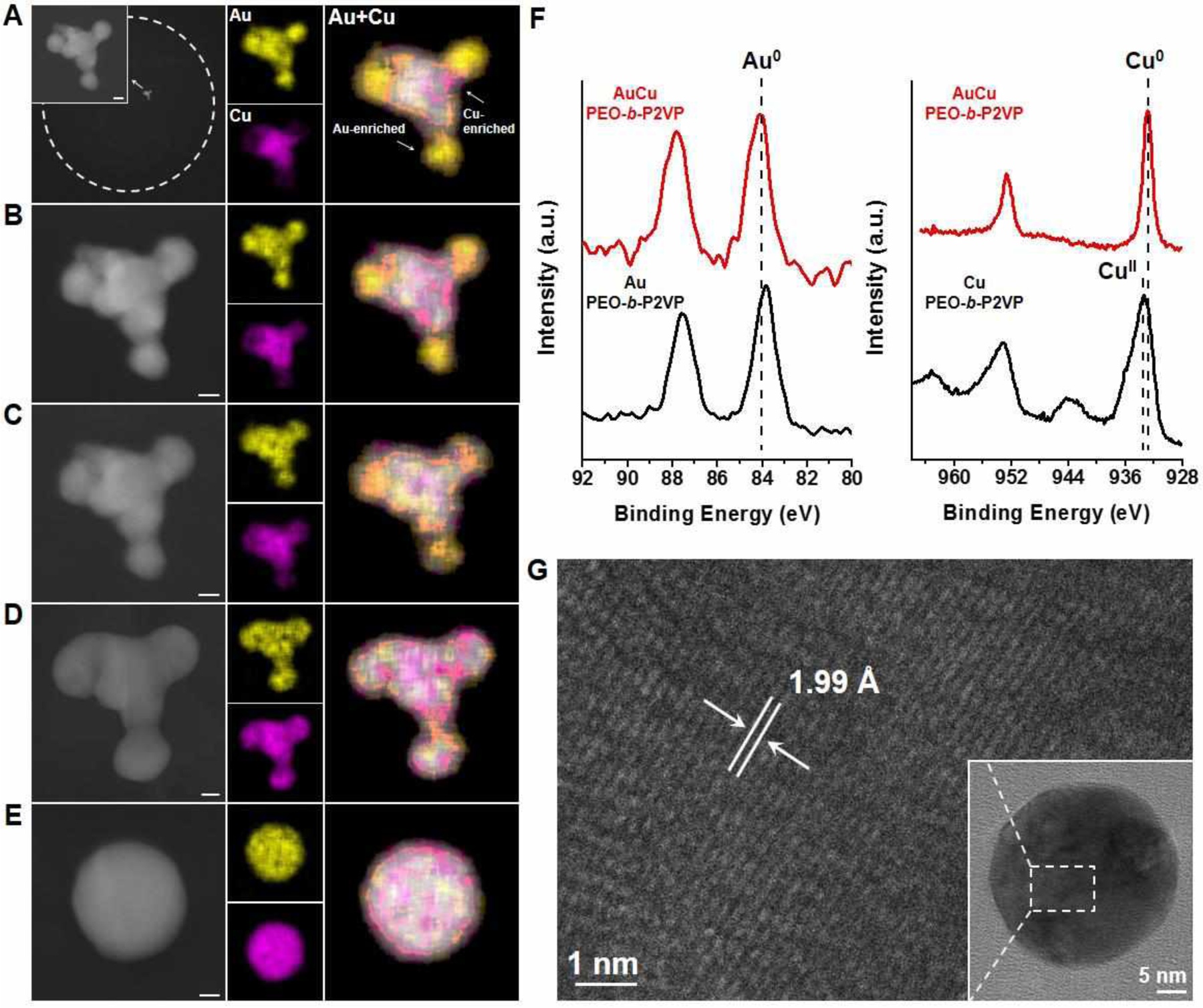
Formation of AuCu nanoparticles in polymer nanoreactors. (A-E) ADF-STEM images and EDS elemental maps of an AuCu particle (44% Au, 56% Cu, atomic composition) formed in a representative polymer feature that contains equal amounts of the metal salt precursors, HAuCl4 and Cu(NO3)2. White dashed circles indicate the edge of polymer features. The polymer feature was stepwise annealed at (A) 160 °C under Ar for 4 h, (B) 240 °C under Ar for 2 h, (C) 240 °C under Ar for 2 h, (D) 260 °C under Ar for 2 h, and (E) 500 °C under H2 for 12 h. Scale bars: 10 nm. (F) Au 4f and Cu 2p XPS spectra of particles synthesized by thermally annealing a drop-cast polymer ink solution at 260 °C for 18 h. Red lines correspond to polymer ink containing both Au and Cu precursors. Black lines correspond to polymer inks containing only one type of precursor. (G) HR-TEM image of an AuCu nanoparticle in a polymer feature that is formed by being annealed at 260 °C for 18h. The observed lattice spacing is 1.99 Å (extracted from fast Fourier transform), which closely matches the AuCu alloy (200) plane.
