Figure 1.
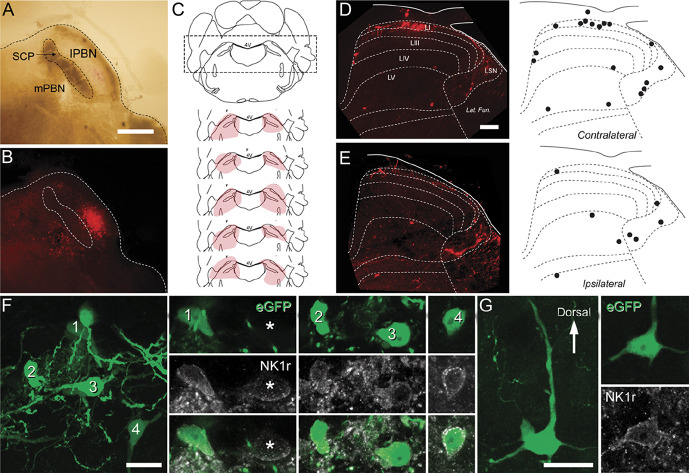
Viral labelling of mouse spinoparabrachial projection neurons (SPBNs). (A) brightfield and (B) fluorescence images show a typical injection site. The superior cerebellar peduncle (SCP) separates the medial and lateral PBN (mPBN and lPBN). In this example (B), mCherry labelling is more prominent in the lPBN than mPBN. (C) Schematic showing bilateral injection sites of AAV9-CB7∼Cl-mCherry into the PBN for retrograde SPBN labelling. Five injection sites (pink shading) are plotted on a representative coronal brain sections that includes the PBN. (D) Transverse section of the L4 spinal cord showing the distribution of retrogradely labelled mCherry SPBNs in both the contralateral (D) and ipsilateral (E) dorsal horn. Labelled cells were more abundant in the contralateral dorsal horn. On both sides, labelled cells were found in lamina I primarily, but also within the LSN and distributed more diffusely within laminae III to V. Distribution plots show the typical pattern of retrogradely labelled cells (black dots). (F and G) Closer inspection of labelled cells after injection of AAV9-CB7∼Cl-eGFP into the SPBN in lamina I (F) and lamina IV (G) showed that most SPBNs (green) showed immunolabelling for NK1 receptor (gray), but these did not account for all NK1 receptor-expressing cells in these laminae (asterisk). Scale bars (in µm): A, B = 500; D, E = 100; F, G = 20. LSN, lateral spinal nucleus.