Fig. 1.
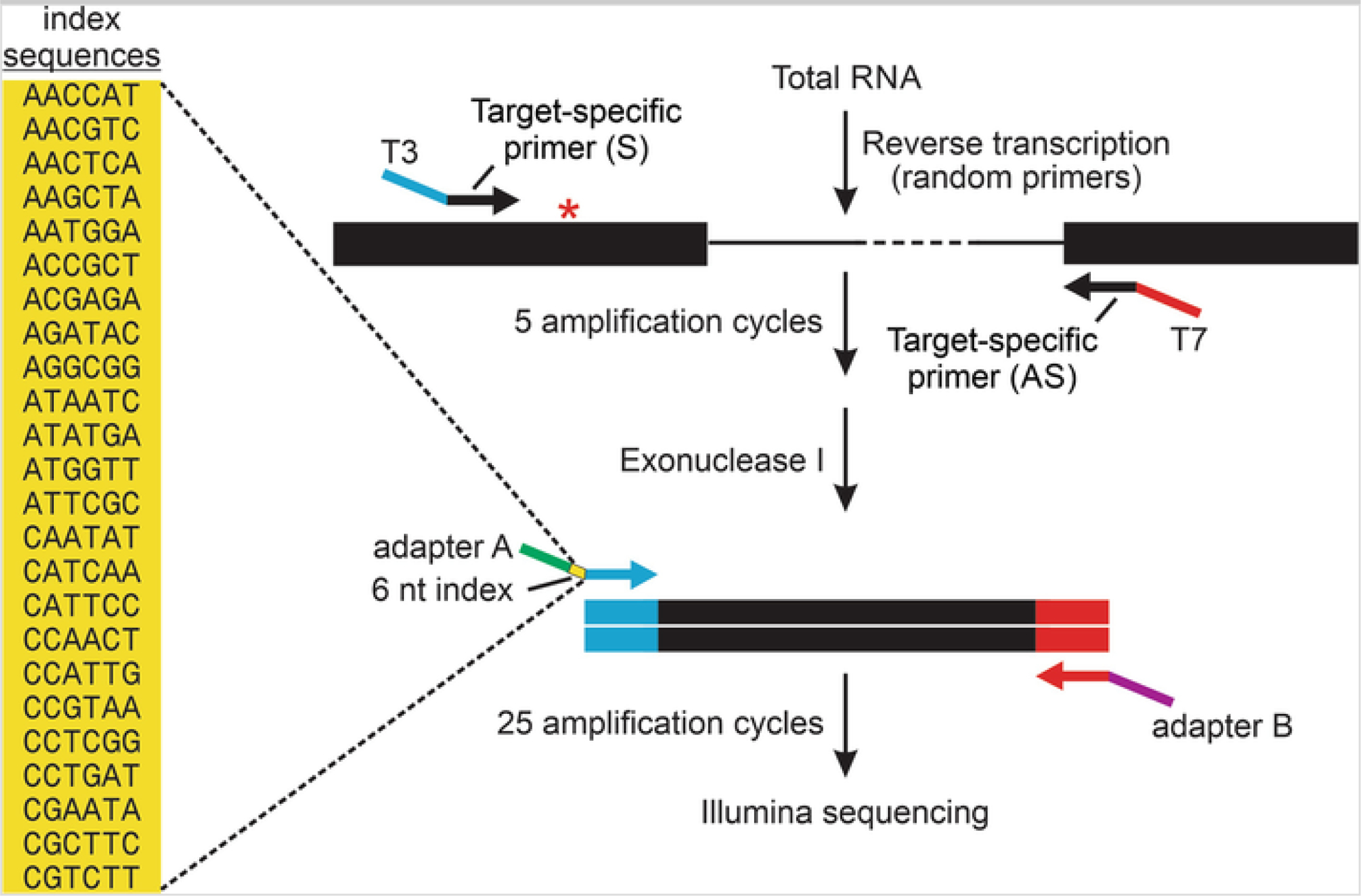
Next-generation sequencing strategy for multiplex quantification of RNA editing profiles. A schematic diagram is presented for RT-PCR amplification of a region of an mRNA target flanking an A-to-I editing site (asterisk). In general, target-specific primers are designed in adjacent exons containing either T3 (blue) or T7 (red) RNA polymerase promoter sequence extensions for the sense and antisense primers, respectively. These primers are used for PCR amplification (5 cycles) before digestion of the remaining single-stranded primers using exonuclease I. A second round of amplification (25 cycles) is performed with universal primers in which the oligonucleotide contains sequences matching the T3 promoter, one of 24 unique 6-nt index sequences (yellow) for sample identification, as well as an adapter sequence (Adapter A; green) or sequences matching the T7 and an adapter sequence (Adapter B; purple) for library preparation and high-throughput single-end sequencing on the Illumina platform
