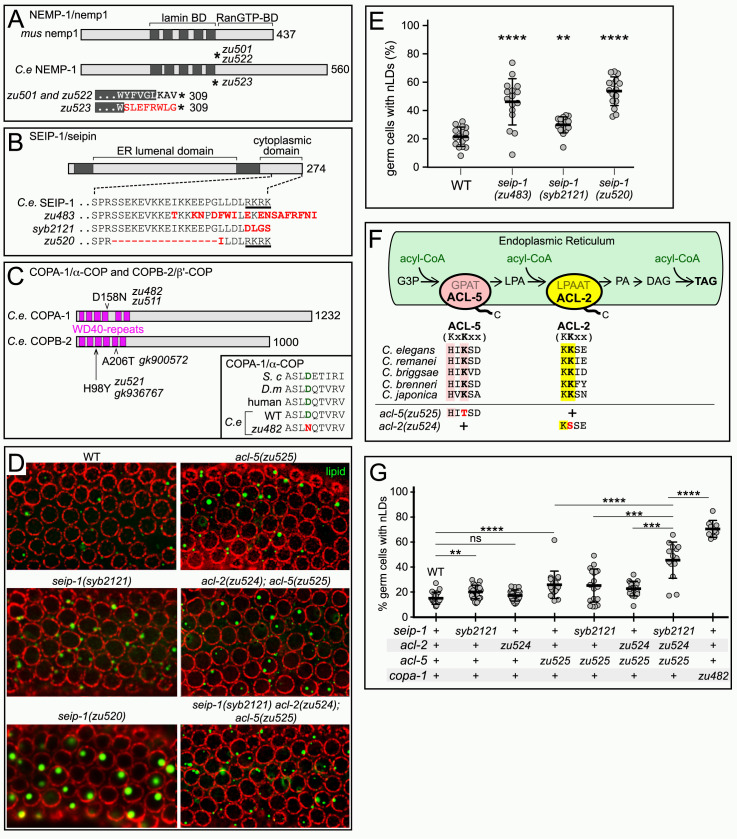
Fig 14. Gene products and analysis of nLD mutants.
(A-C) Diagrams of wild-type and mutant protein products as listed. Dark grey boxes (NEMP-1, SEIP-1) indicate transmembrane domains, and protein sizes in amino acids are indicated to the right of each cartoon; amino acid replacements in the mutant proteins are shown in red, and stop codons are indicated by asterisks. The diagrams list both the original mutations (zu501, zu483, and zu482) identified in our genetic screens and mutations generated by gene editing. Both nemp-1(zu501) and nemp-1(zu522) result in identical truncated proteins, but the stop codon in nemp-1(zu523) results from a different frameshift that alters the intervening amino acids; BD = binding domain. seip-1(zu483) is a point mutation that causes a I260T substitution, followed by a 2 base pair deletion that shifts the reading frame of the C-terminus. copa-1(zu482) and copa-1(zu511) are identical mutations, but isolated in separate screens (see text). The mutations copb-2(gk900572) and copb-2(gk936767) are in strains identified by the C. elegans Million Mutation Project. (D) nLDs in the peak zones of wild-type or mutant gonads as labeled. The seip-1(syb2121) mutant lacking the presumptive retrieval peptide RKRK has slightly more nLDs than wild type, but the nLDs are fewer and smaller than in seip-1(zu483) mutants. Conversely, the seip-1(zu520) mutant, which retains the retrieval peptide but lacks adjacent residues, has both larger and more numerous nLDs than wild type. The acl-5 mutant has more nLDs than wild type, and the triple seip-1acl-2; acl-5 mutant has considerably more nLDs. (E) Plot of seip-1 mutant germ cells with nLDs, as for Fig 14D. (F) Diagram showing a fat synthesis pathway involving the ER-resident membrane proteins ACL-5/GPAT and LPAAT/ACL-2. These proteins have conserved, predicted C-terminal retrieval motifs of the form KxKxx and KKxx, with the -3 lysine being the most critical residue. Gene editing was used to change the -3 residue, creating acl-5(zu525) and acl-2(zu524) mutants. G3P (glycerol-3-phosphate), GPAT (G3P acyltransferase), glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase) LPA (lysophosphatidic acid), LPAAT (LPA acyltransferase), PA (phosphatidic acid), DAG (diacylglycerol), TAG (triacylglycerol). (G) Plot of germ cells with nLDs, as for Fig 14D. Points in graphs represent individual gonads; plot shows mean and standard deviation. P value from unpaired t test with Welch’s correction**** P< 0.0001, ***P ≤ 0.01, **P ≤ 0.01, ns not significant.