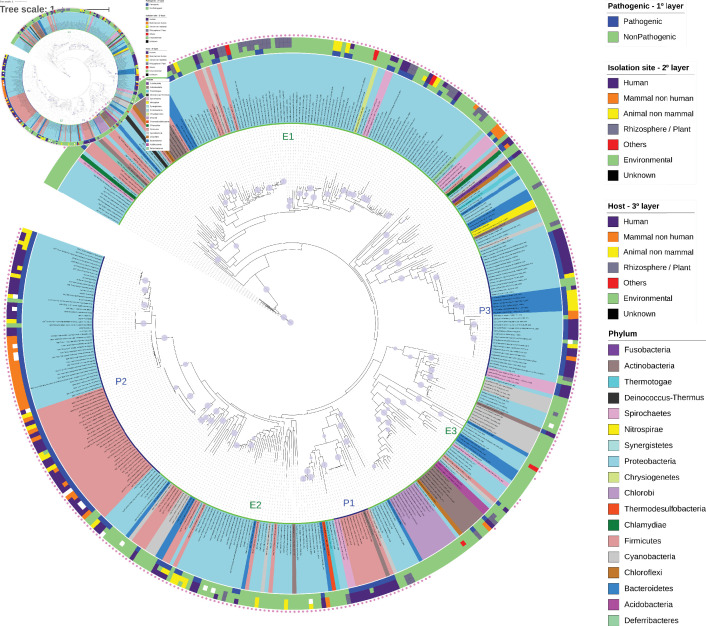
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic tree of NeuB sequences retrieved from the KEGG database. The NeuB sequences were retrieved from the KEGG database using ID K01654. The taxon ID associated with each sequence was used to identify the species from which the sequence originated and to extract metadata related to lifestyle, isolation site and host. NeuB sequences were trimmed to the NeuB domain and then aligned using MAFFT in the default configuration. The alignment was used to infer the phylogenetic relationships through the ML method on the IQTree server. The automatic bootstrap, suggested by IQTree, ended with 456 replicates. The completed tree was viewed and edited in the iTOL program. The species names are displayed at the end of each branch. The colours of the species names represent the phylum to which they belong. The first layer after the species name represents the lifestyle. The second layer represents the isolation site, and the third layer represents the identified host. The outermost pink dot indicates the presence of the SAF domain in the respective sequence. Clusters of pathogenic (P1, P2 and P3, inner blue line) and environmental (E1, E2 and E3, inner green line) bacterial species are indicated. The purple dots on the tree branches represent bootstrap values above 75 %. Bar, 10 amino acid substitutions per site per million years.