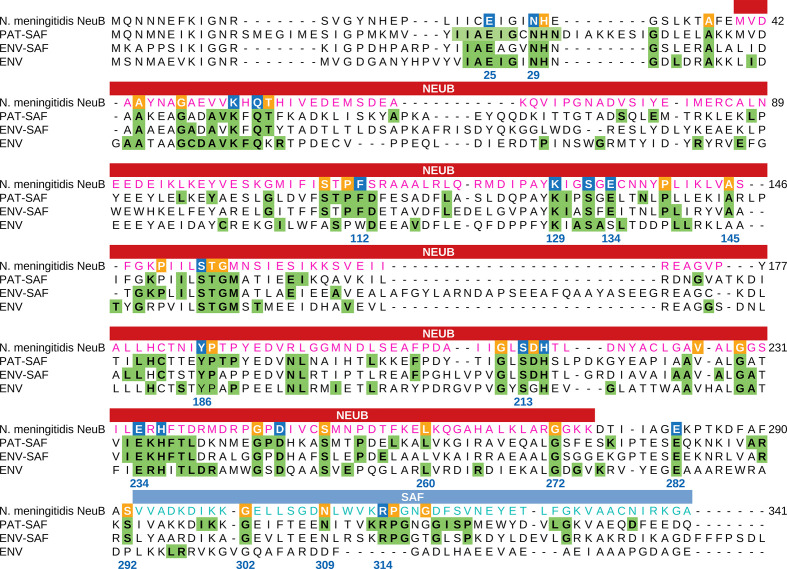
Fig. 2.
Comparison between the NeuB sequence of N. meningitidis and the NeuB sequence profiles of pathogenic and environmental bacteria. The sequences identified as NeuB in the KEGG database were divided into three groups: PAT-SAF, NeuB from pathogenic bacteria with an SAF domain (n=169); ENV-SAF, NeuB from environmental bacteria with an SAF domain (n=202); and ENV, NeuB from environmental bacteria without an SAF domain (n=40). Each group of sequences were aligned separately using MAFFT. The alignments were used to build a conservation profile for each group considering each amino acid residue in each position. The tree profiles were compared with the NeuB sequence of N. meningitidis . The residues important for catalysis were identified by Gunawan et al. [19] based on the NeuB structure crystallized with its substrates ManNAc and PEP. The positions marked in blue in the N. meningitidis sequence represent catalytic residues, while the positions marked in orange represent non-catalytic residues. Green tagged residues in the profiles represent positions with at least 70 % conservation in the alignment. The amino acid residue positions listed in the alignment are related to NeuB of N. meningitidis . The NeuB domain and the SAF domain are indicated in the box above the alignment.