Fig. 2. Characterization of OptoAAV system components.
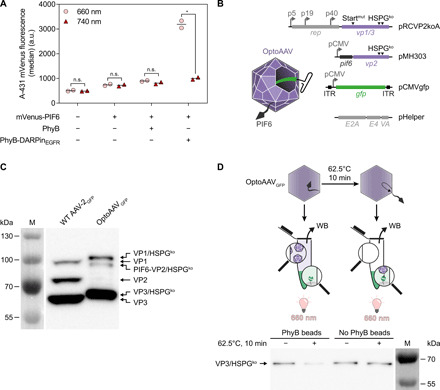
(A) Light-controlled recruitment of mVenus-PIF6 to cells. A-431 cells were incubated with 100 nM PhyB or PhyB-DARPinEGFR and/or 200 nM mVenus-PIF6 for 20 min under 740- or pulsed 660-nm light. Afterward, cellular mVenus fluorescence was analyzed by flow cytometry. n > 2200 cells per sample. Mean is indicated. n.s. (not significant), P ≥ 0.05; *P < 0.05. a.u., arbitrary units. (B) Construction of OptoAAVs. OptoAAVs were produced in HEK-293T cells by cotransfection of four plasmids. pRCVP2koA encodes nonstructural proteins required for replication (rep) and the viral capsid proteins VP1 and VP3. Expression of vp2 was prevented by a silent mutation within the vp2 start codon T138 (Startmut), and the natural HSPG tropism was ablated by two mutations (R585A and R588A; HSPGko). pMH303 encodes PIF6 fused to VP2 (HSPGko) under the CMV promoter. pCMVgfp contains a self-complementary AAV genome encoding GFP. pHelper provides adenoviral genes for AAV production. ITR, inverted terminal repeat. (C) Western blot (B1 antibody) against capsid proteins of wild-type (WT) AAV-2GFP and OptoAAVGFP. Representative data of n = 3 batches. M, protein size marker. (D) Binding of OptoAAVGFP to PhyB. OptoAAVsGFP (optionally preincubated at 62.5°C for 10 min) were incubated with or without PhyB-functionalized beads under 660-nm light for 1 hour. After pelleting beads, supernatants were analyzed for unbound OptoAAVGFP by Western blot (WB; B1 antibody) against VP3. Representative data of n = 4 experiments.
