Fig. 6. Activation mechanism of CC chemokine receptors.
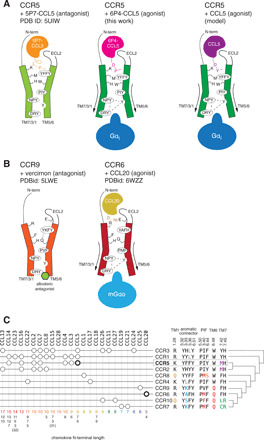
(A) CCR5 bound to the antagonist [5P7]CCL5 (left, orange), the super-agonist [6P4]CCL5 (center, magenta), and the natural agonist CCL5 (right, purple). Key residues in the activation mechanism of CCR5 are shown. (B) Proposed activation mechanism for CCR6 by CCL20 (yellow, right) by comparing with the structure of CCR9 (left). (C) Pairing between CC chemokine receptors and CCL chemokines (59). At the right, the sequence composition of key positions is shown, together with the phylogenetic relationship between the receptors. The lengths of the CCL chemokine N termini according to UniProt (60) are shown at the bottom. The available active CCR/CCL complex structures are shown in bold.
