Fig. 1. iSILK strategy to probe evolving plaque pathology using multimodal chemical imaging.
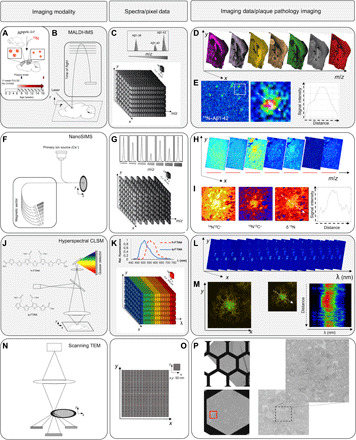
(A) APPNL-G-F mice were fed 15N diet, leading to metabolic isotope incorporation into APP and release and deposition of labeled Aβ peptide that is delineated with IMS. (B) MALDI-IMS uses a laser for analyte desorption and ionization and allows detection of intact Aβ peptides at 10 μm (C). (D) MALDI single ion images outline different Aβ isotopologues across the brain at a single plaque level (E). Here, total 15N–Aβ1-42 [Σ mass/charge ratio (m/z) 4450 to 4465] localizes predominantly to the plaque core. (F) NanoSIMS uses a highly focused, high-energy, primary ion beam for analyte desorption and ionization, allowing imaging of polyatomic species at 50 nm with high sensitivity with up to 7 m/z channels in parallel (G and H). NanoSIMS allows quantification of stable isotope enrichment (15N/14N above natural 15N abundance) at nanoscopic structures such as single plaques, although without intact molecular information. (I) Here, predominant 15N enrichment is detected at the core. (J to P) IMS is complemented with light and electron microscopy (EM) for additional structural information. (J to M) Structural amyloid imaging with confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) and hyperspectral detection. (J) Double LCO staining with tetrameric formyl thiophene acid (q-FTAA) and heptameric formyl thiophene acid (h-FTAA). q-FTAA binds preferentially to mature fibrils. h-FTAA recognizes both mature and immature, prefibrillar Aβ. (K) The LCO probes have different emission properties that are delineated by CLSM using a spectral detector providing a continuous emission spectrum (32+2 channels) within each pixel (K), generating a lambda stack (L). Linear unmixing generates normalized emission profiles across single plaque and structural annotation based on the LCO emission profile (M). A characteristic blue shift is observed at the core indicating q-FTAA binding and mature, amyloid fibril content. (N) Scanning transmission EM (STEM) imaging on embedded tissues samples before NanoSIMS. STEM provides ultrahigh resolution at low nanometers (O), allowing visualization of fibrillar content in single plaques (P).
