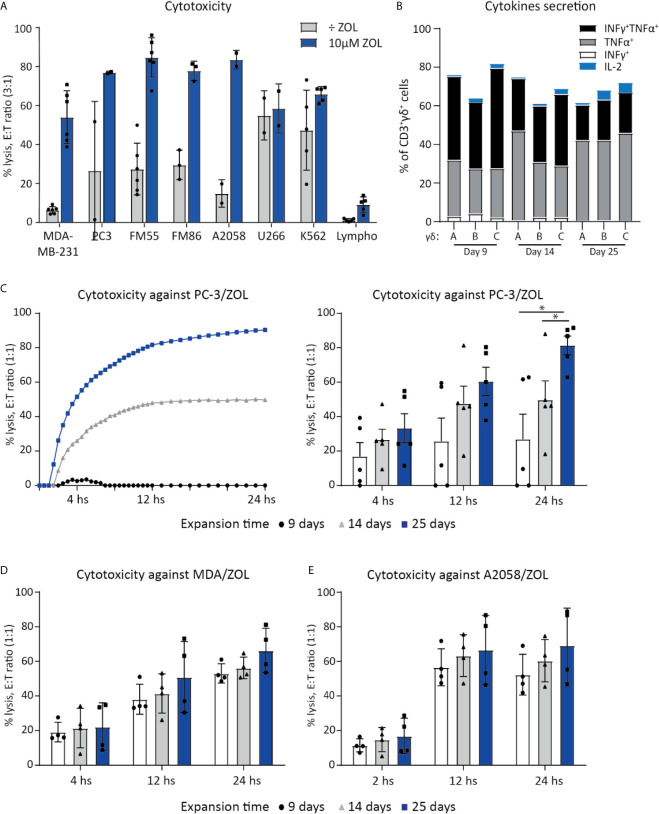
Figure 1.
Vγ9Vδ2 T cell can efficiently kill cancer cells. (A) Chromium release assay (4 h) was used to test Vγ9Vδ2 T cell ability to kill cancer cell lines of various origins. Vγ9Vδ2 T cells were expanded from healthy donors (n =2-6). Effector cell (E:T) Target cell ratio (3:1). Breast cancer cell line = MDA-MB-231, Prostate cancer cell line = PC-3. Melanoma cells lines = FM55, FM86 and A2058. Hematological cancer cells lines = U266 and K562. Lymphocytes (lympho) were thawed and rested overnight prior to the assay. Vγ9Vδ2 T cell cultures used in these assays had been in culture for 14-30 days prior to the chromium release assays. Purity >90% for Vγ9Vδ2 T cell cultures was verified by flow cytometry (data not shown, see gating strategy in Supplementary Figure 1A ). (B) Cytokine expression of day 9, 14 and 24 expanded Vγ9Vδ2 T cells was determined by gating on positive cells in PC-3/ZOL co-cultured with Vγ9Vδ2 T cells. Gates were set according to PC-3 co-cultured control. Three different Vγ9Vδ2 T cell cultures were analyzed, named A, B and C (C) Vγ9Vδ2 T cells ability to kill PC-3/ZOL cancer cell line was compared between cultures expanded for 9, 14 or 25 days, using a 24 h xCELLigence assay at effector-target cell ratio (1:1). The left graph depict one donor, showing the full 24 h xCELLigence assay, and the right graph summarizes the data from five donors (n=5 donors, repeat three times) (D) Comparison of percentage cytolysis at effector-target cell ratio (1:1) in xCELLigence assay, assessing Vγ9Vδ2 T cells expanded for 9, 14 or 25 days, targeting MDA-MD-231/ZOL (MDA). (n=3 donors, repeat twice) (E) Comparison of percentage cytolysis at effector-target cell ratio (1:1) in xCELLigence assay, assessing Vγ9Vδ2 T cells expanded for 9, 14 or 25 days, targeting A2058/ZOL (MDA). (n=3 donors, repeat twice). Statistical significance was determined by a paired T-test. *P ≤ 0.05. Error bars indicated standard error of mean (SD).