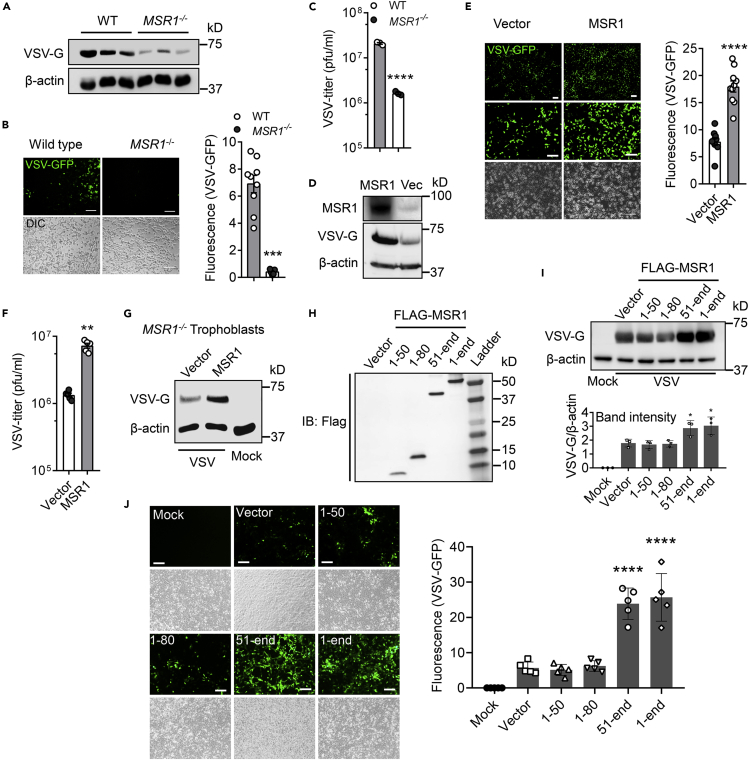
Figure 5.
MSR1 facilitates cellular entry of VSV through its extracellular domains
(A–C) WT and MSR1−/− trophoblasts were examined at 12 h after VSV-GFP inoculation, (A) immunoblots of VSV-G protein level, (B) VSV-GFP fluorescence intensity, and (C) VSV titers in the cell culture medium, MOI = 0.5. N = 3 biological replicates.
(D–F) WT and MSR1-overexpressed trophoblasts were examined at 12 h after VSV-GFP inoculation, (D) MSR1 protein expression, VSV-G protein level, (E) VSV-GFP fluorescence intensity, and (F) VSV titers in the culture medium, MOI = 0.5. N = 3 biological replicates. The VSV-GFP fluorescence intensity in (B) and (E) was acquired with a fluorescence microscope from 9 random fields of three biological replicates and quantified by ImageJ. Objective: 4x (top) and 20x, scale bar: 100 μm.
(G) Immunoblots of VSV-G protein level in MSR1−/− trophoblasts with epichromosomal complementation of an empty vector or FLAG-MSR1 expression plasmid at 12 h after VSV infection, MOI=0.5.
(H) The protein expression of different FLAG-tagged MSR1 fragments at 24 h after transfection of plasmids in trophoblasts. IB: immunoblotting. Amino residues 1-50 (cytoplasmic N-tail), 1-80 (cytoplasmic N-tail plus transmembrane), 51-end (extracellular domains with transmembrane), and 1-end (full length).
(I) VSV-G protein level and (J) VSV-GFP fluorescence intensity in trophoblasts overexpressing FLAG-MSR1 fragments at 12 h after VSV-GFP infection at an MOI = 0.5. The GFP fluorescence intensity was acquired with a fluorescence microscope from random regions of three biological replicates (N = 3). β-actin is a housekeeping control. Mock: no virus infection control. Scale bar: 100 μm. All the data are presented as mean ± S.E.M., and statistical significances are analyzed by a standard two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, compare with WT or vector.