FIGURE 1.
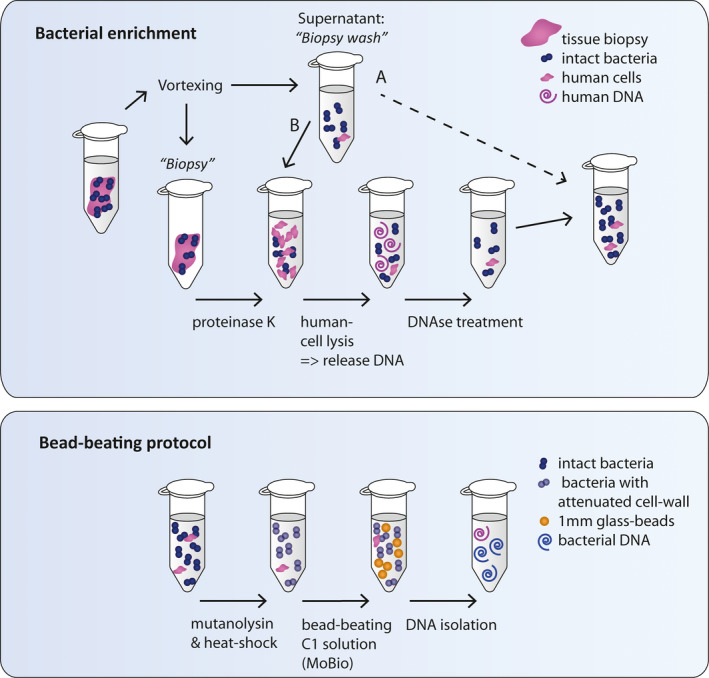
Schematic drawing of DNA isolation protocol strategy 2. (a) Bacterial enrichment: A tissue biopsy is vortexed in PBS to separate bacteria from the biopsy. The biopsy is retrieved for digestion with proteinase K, while the supernatant (biopsy wash) is saved on ice and added back for DNA isolation at a later timepoint (timepoint A or B; B in the final protocol). Bacteria in the biopsy wash are thereby minimally exposed to reagents that could cause possible lysis; however, this suspension contains human cells and/or released human DNA and should therefore follow route B. Subsequently, 0.0125% saponin in PBS is added to the cell suspension inducing lysis of human cells, but not bacterial cells. DNA in the supernatant is depleted through DNAse treatment. The remaining sample has reduced human DNA content and still intact bacteria. (b) Bead‐beating protocol: The sample is further processed by our previously optimized bead‐beating protocol. Mutanolysin treatment followed by heat shock is applied to attenuate cell walls of Gram‐positive bacteria (e.g., Streptococci and Actinobacteria) to make them more susceptible for mechanical lysis. Subsequently, the sample is bead‐beaten with 1 mm glass beads in C1 buffer of the PowerLyzer PowerSoil DNA Isolation Kit and further isolated according to the manufacturer's protocol. The resulting DNA isolate is enriched for bacterial DNA
