Figure 7.
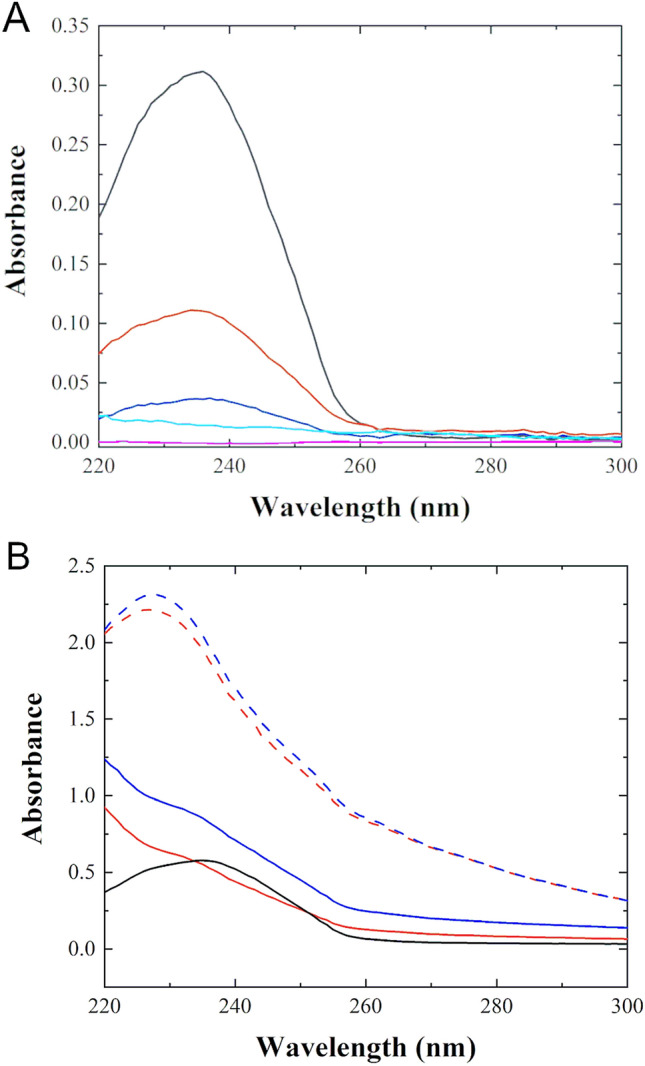
Absorbance measurements from vesicles containing a polyunsaturated lipid exposed to Cu2+ and piscidin bound to Cu2+. SUVs made of 3:1 DLPC/POPG were prepared and exposed to different forms and amounts of Cu2+ and measured by UV spectrophotometry after 24 h of exposure. (A) Samples containing SUVs at a fixed lipid concentration of 0.50 mg/mL (640 µmol/L) were mixed with various amounts of CuCl2, as follows: Cu2+/L = 1:2 molar ratio (black), Cu2+/L = 1:8 (red), Cu2+/L = 1:32 (blue), BHT/L = 1:100, and Cu2+/L = 1:8 (cyan) and lipid alone (magenta). (B) SUVs at a concentration of 0.20 mg/mL (260 µmol/L) were studied in the presence of the peptides at P/L = 1:10, corresponding to a peptide-Cu2+ complex concentration of 26 µmol/L. P1-Cu2+ (blue, dashed); P3- Cu2+ (red, dashed); P1 (blue); P3 (red); lipid alone (black). The source of free Cu2+ (CuCl2) was the same as that used for metallating P1 and P3. Measurements were taken in triplicates at 24 h after exposure. The spectra were corrected for the background signals from CuCl2 and the lipids at time zero as explained in the Methods. Uncertainties are smaller than the line thicknesses. Strong absorbance at 234 nm after 24 h of exposure points at the formation of lipid oxidation products, a result confirmed by mass spectrometry (Fig. S7).
