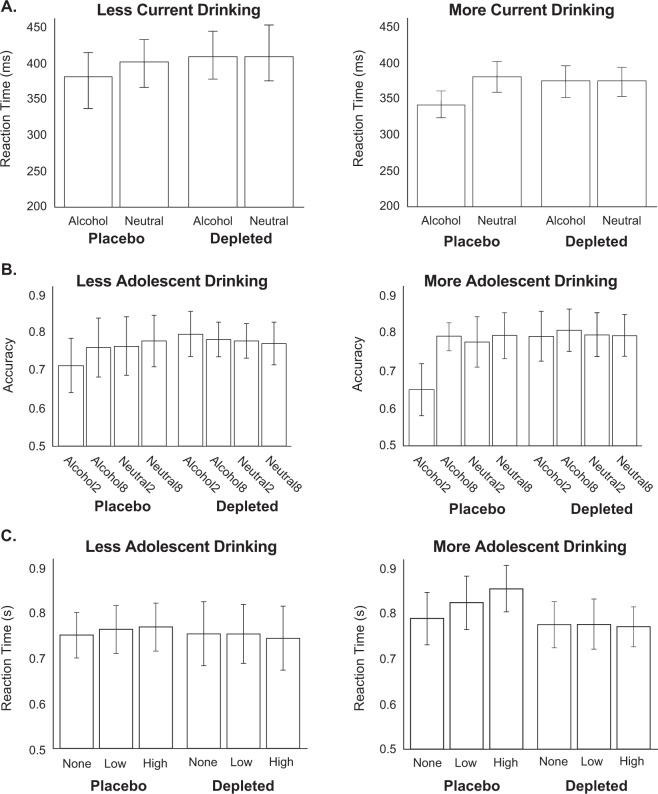
Fig. 1. Dopamine depletion attenuates attentional bias, dependent on binge drinking severity.
A For the dot-probe task, a linear mixed model indicated a significant beverage type × cue type × current binge drinking interaction effect on RT. B For the attentional blink task, a linear mixed model indicated a significant beverage type × cue type × lag × adolescent binge drinking interaction effect on accuracy. C For the reward task, a linear mixed model indicated a significant beverage type × distractor type × adolescent binge drinking interaction effect on RT. Least squares means are presented. For display purposes, binge drinking was binarized: “More Current Binge Drinking” corresponds to an Alcohol Use Questionnaire binge score of >10, whereas “More Adolescent Binge Drinking” corresponds with >9 estimated binge episodes by the age of 21.