Figure 2. One-Week Treatment With Autologous Antimicrobial-Producing Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus (CoNS-AM+) Decreases Proportion of Staphylococcus aureus in the Microbial Community Without Leading to Excess Bacteria Accumulation on the Skin Surface.
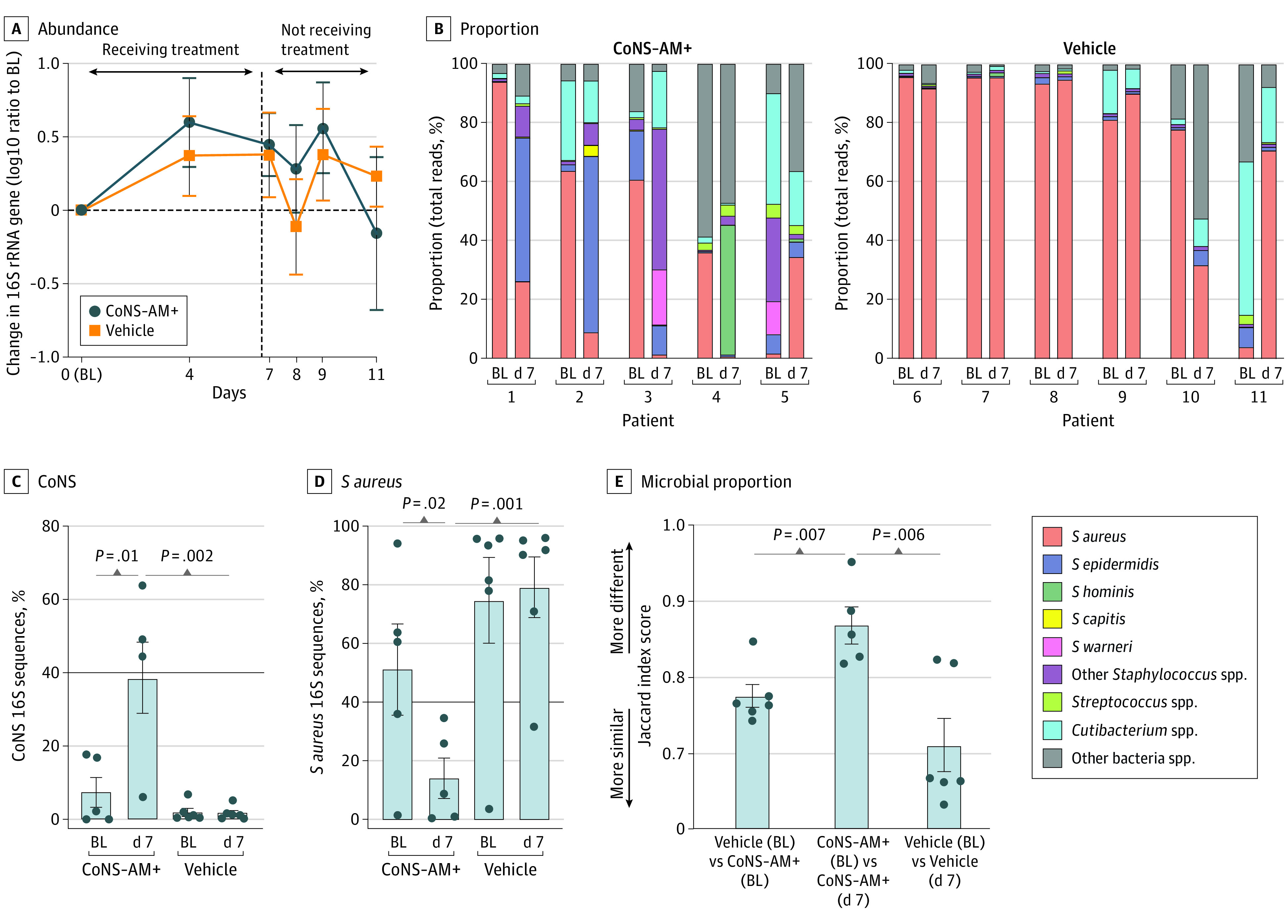
Effect of topical application of CoNS-AM+ or vehicle on the abundance (A) and proportion (B) of total 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene on the surface of lesional skin of patients with atopic dermatitis (AD). Data represent the mean (SEM) from each arm of individual patients. Data were compared with a 2-tailed parametric unpaired t test. The following CoNS-AM+ was transplanted to each patient: patient 1, Staphylococcus epidermidis-N009-G7; patient 2, Staphylococcus epiermidis-N018-F3; patient 3, Staphylococcus warneri-N025-G2; patient 4, Staphylococcus hominis-N005-E10; and patient 5, Staphylococcus capitis-N030-H8 (eFigure 1B in Supplement 2); spp indicates species. Relative abundance of CoNS (C) and S aureus 16S rRNA genes (D) determined from panel B. Data represent mean (SEM). Data were compared with a 2-tailed parametric paired (between points within the same group) or unpaired (between different treatment groups) t test. E, Dissimilarity in the microbial proportion calculated based on the Jaccard distance of the data from panel B. The P value was calculated by a 2-tailed parametric paired (baseline [BL] vs day 7 within the same patient’s group) or unpaired (BL data between different treatment group) t test.
