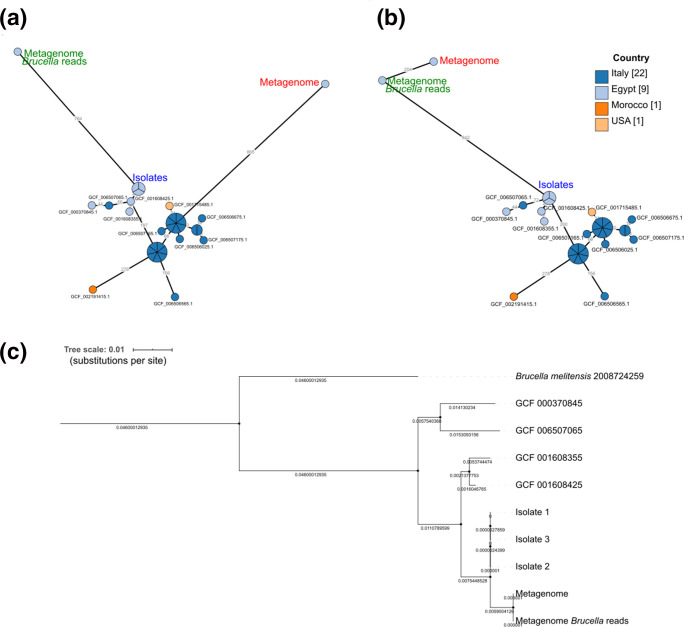
Fig. 4.
Genomic typing of Brucella from Egyptian raw milk samples by cgMLST (a, b) and SNP analysis (c) using WGS and WMS datasets. (a) Excerpt of a minimum spanning tree (Fig. S4 gives an overview) based on cgMLST allelic profiles of 336 publicly available genomes, and assemblies of WGS and WMS data from raw milk sample number 151. Assemblies from WMS data were generated either by metagenomic assembly (metagenome) or after extraction of Brucella -specific reads (metagenome Brucella reads). Numbers at the branches stand for allelic distances, and branches presenting less than 10 alleles difference are collapsed. Assemblies of WGS data of isolates and Brucella -specific reads were generated either with Shovill and SPAdes, respectively (a), or with megahit (b). (c) Phylogenetic relationship of four closely related publicly available draft genomes and WGS and WMS data obtained from raw milk sample number 151 based on core SNP distances illustrated in a maximum-likelihood tree.