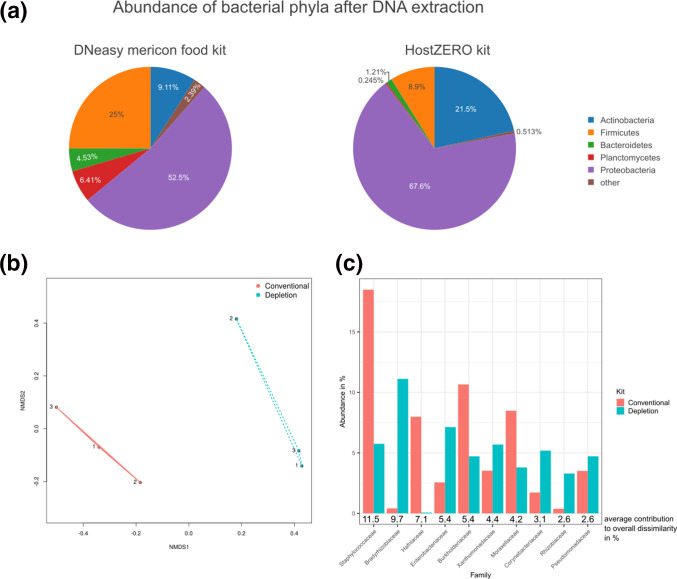
Fig. 5.
Analysis of the effects of different DNA extraction strategies on the abundance of bacterial phyla in pure cow’s milk. The prokaryotic composition of raw milk used for inoculation experiments was determined by KrakenUniq after conventional DNA extraction with the DNeasy mericon food kit, and after eukaryotic cell depletion and DNA extraction with the HostZERO kit. (a) Mean abundances (%) of the bacterial phyla most prevalent in three replicates are presented in a pie chart for each extraction kit. (b) Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) analysis based on Bray–Curtis dissimilarity of the detected bacterial families in all samples after conventional DNA extraction (red) and DNA extraction with eukaryotic cell depletion (blue). (c) Mean abundances (%) of the families that were most discriminating between the two DNA extraction kits obtained by analysis of similarity percentage (SIMPER) using Bray–Curtis dissimilarity are presented in a bar chart together with the mean contribution to the overall dissimilarity.