Figure 2.
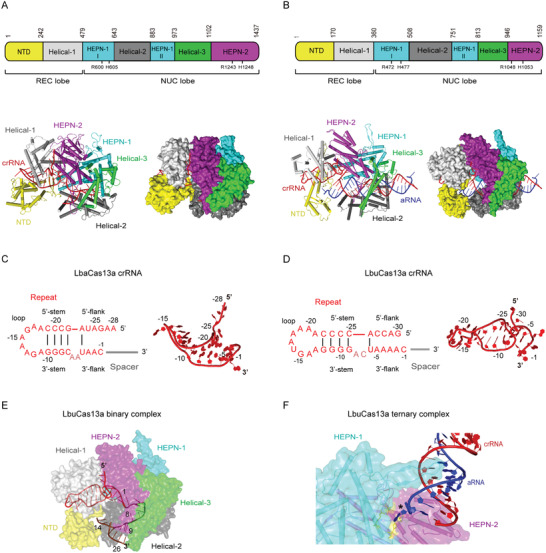
Structural features of type VI‐A CRISPR‐Cas effectors. All structural figures were generated in PyMOL (http://pymol.org). A,B) Top: linear domain organization of Lahnospiraceae bacteriumCas13a (LbaCas13a) (A) and Leptotrichia buccalis Cas13a (LbuCas13a) (B) with the HEPN nuclease active site residues, REC and NUC lobes annotated. All figures use the same color code unless otherwise stated. Bottom: cartoon and surface representations of the overall structure of the LbaCas13a‐crRNA binary complex (PDB ID: 5W1H)(A) and LbuCas13a‐crRNA‐aRNA ternary complex (PDB ID: 5XWP)(B). Domains are colored according to the linear domain organization diagram, crRNA is colored red and activator RNA (aRNA) is colored blue. C,D) Left: diagram of the LbaCas13a‐crRNA (C) and LbuCas13a‐crRNA (D) secondary structure. Because the focus of the diagram is structure and sequence of the repeat region, spacer nucleotides were omitted and spacer region is represented by a gray line. Subregions of the repeat region are annotated, and Watson–Crick base pairs are denoted with black lines. Dinucleotide bulge residues are indicated in a lighter shade of red. Right: 3D structure of the crRNA repeat region from the LbaCas13a‐crRNA binary complex (PDB ID: 5W1H)(C) and LbuCas13a‐crRNA‐aRNA ternary complex (PDB ID: 5XWP)(D). Nucleotides belonging to repeat region are colored and annotated according to the diagram on the left, whereas spacer nucleotides were entirely omitted. E) View of conformations and locations of crRNA spacer subregions in LbuCas13a‐crRNA binary complex (PDB ID: 5XWY). LbuCas13a is shown as partially transparent surface representation in order to distinguish concealed and solvent‐exposed subregions of crRNA. Domains of LbuCas13a are colored according to panel (B), crRNA repeat region is colored red, and spacer is colored brown. Marked nucleotides denote borders of each spacer subregion: nucleotides 1–8 correspond to the conformationally distorted 5′ part of spacer located in NUC lobe, whereas nucleotides 9–14 and 15–26 correspond to the solvent‐exposed central seed region and the 3′ part of spacer, respectively. F) View of the interactions between aRNA and LbuCas13a HEPN nuclease active site. The active‐site proximal β‐hairpin from HEPN‐1 domain extends into a helical groove formed by the crRNA‐aRNA duplex, guiding the 5′‐terminal nucleotide of aRNA into the pocket in which the active site is located. crRNA is colored red, aRNA is colored blue, and LbuCas13a is shown as a mixed surface‐cartoon representation with partially transparent surface. The active site residues R472, H477, R1048A, and H1053A are colored yellow and the 5′‐terminal nucleotide of aRNA is indicated with asterisk (*).
