Figure 6.
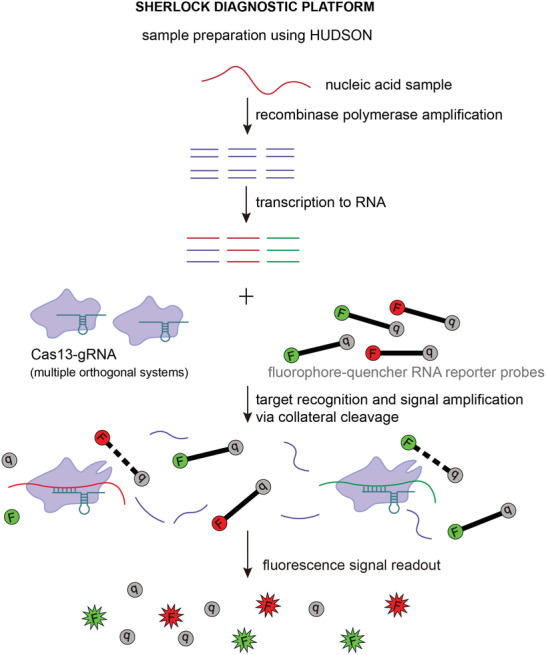
Schematic representation of Cas13‐based nucleic acid detection using SHERLOCK (specific high‐sensitivity enzymatic reporter unlocking) diagnostic platform. SHERLOCK harnesses the nonspecific ssRNA cleavage activity of Cas13 effectors exhibited after detecting the guide RNA‐complementary RNA sequence to determine the presence and quantify the amount of certain nucleic acid species in a sample. Briefly, collected samples are first treated using HUDSON (heating unextracted diagnostic samples to obliterate nucleases), after which nucleic acid samples are converted to cDNA via recombinase polymerase amplification and then reverted to RNA by T7 transcription. The sample is then mixed with short RNA reporter fragments (e.g., poly‐U or poly‐A sequences) containing a fluorophore‐quencher pair. Incubation with Cas13 and target‐specific guide RNA initiates Cas13‐mediated nonspecific ssRNA cleavage, including cleavage of ssRNA reporters that emit fluorescent light proportionally to the amount of targeted nucleic acid species, which enables visualization and quantitation of results via fluorescence or colorimetric lateral flow readout. SHERLOCK can be used for diagnosing viral and other infectious diseases, cancer mutations, health‐related single nucleotide polymorphisms, genetic traits in plants, etc.
