Figure EV5. Residue Q498H substitution in GD/1/2019 RBD and GX/P2V/2017 RBD strengthens the interaction with the receptor compared with the SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD.
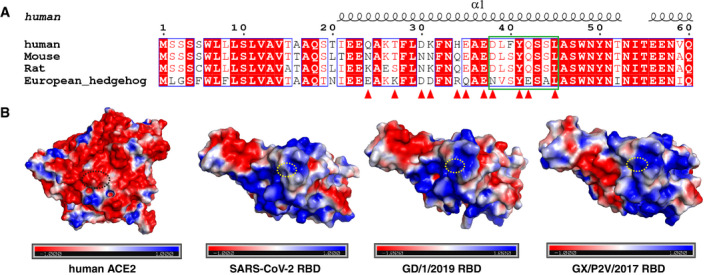
- Sequence alignment of the ACE2 sequences from human, mouse, rat, and European hedgehog. The residues of hACE2 binding with GD/1/2019 RBD are indicated in red triangles, and residues from hACE2 binding with the residue 498 of RBD are indicated in green box. Identical residues are highlighted in red background, and similar residues are labeled in red and boxed in blue lines.
- The surface of hACE2, SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD, GD/1/2019 RBD, and GX/P2V/2017 RBD (left to right) colored for electrostatic potential: blue (basic), white (neutral), and red (acidic) at ± 1 kTe−1. Residues from hACE2 binding with the residue 498 of RBDs are circled with black dotted ellipse, and residues Q498, H498, and H498 of SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD, GD/1/2019 RBD, and GX/P2V/2017 RBD are circled with yellow dotted ellipse.
