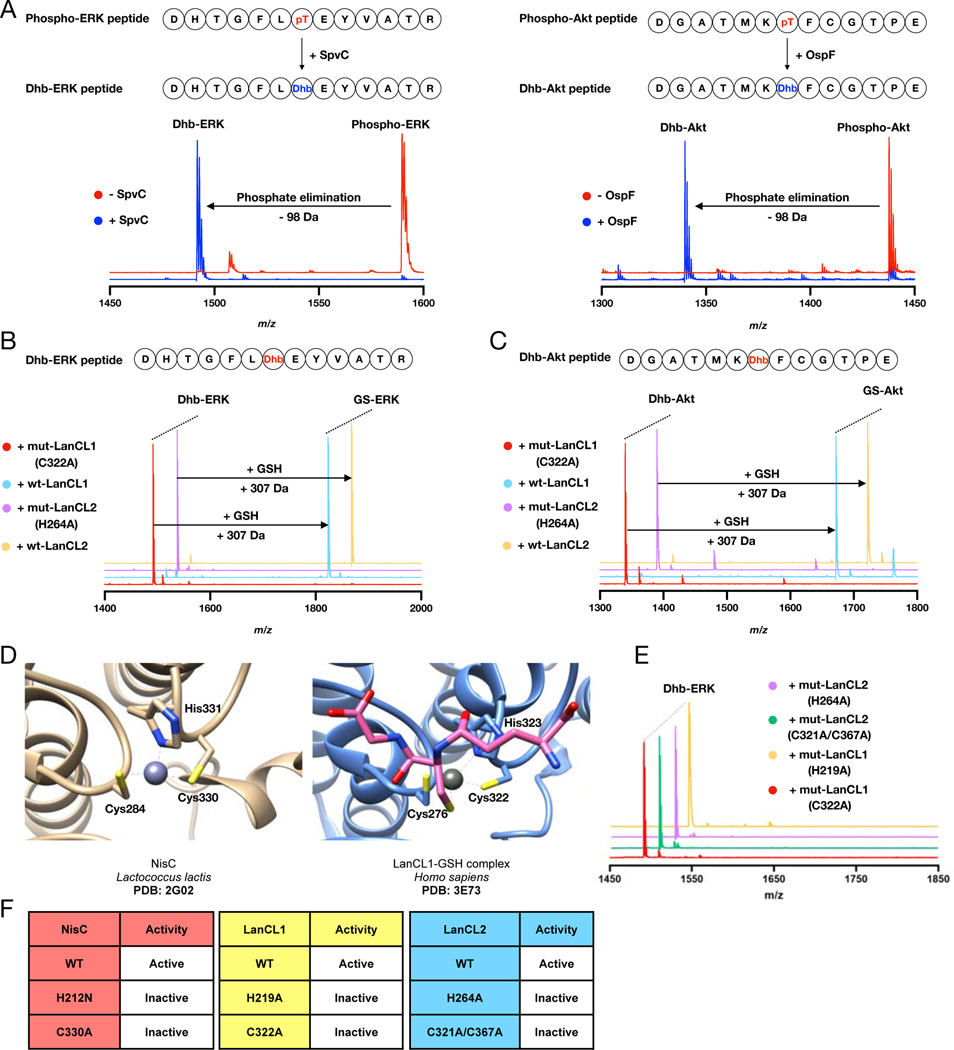
Figure 2. Eliminative damage in peptides catalyzed by the pathogen pThr lyases SpvC or OspF and addition of GSH to these eliminated peptides by wt LanCL1 and LanCL2 but not mutants.
(A) MALDI-TOF mass spectra of phospho-ERK peptide treated with His6-SpvC and phospho-Akt peptide treated with His6-OspF resulting in a loss of 98 Da. See Supplemental Table 2 for calculated and observed masses and Figure S1C for fragmentation data. (B) MALDI-TOF mass spectra of Dhb-containing ERK peptide treated with wt LanCL1- and 2 or mutants in the presence of GSH. (C) MALDI-TOF mass spectra of Dhb-containing Akt peptide treated with wt LanCL1 and LanCL2 or mutants. (D) Active sites of LanCL1 bound to GSH (PDB ID 3E73) and the intra-molecular C-S bond forming catalyst NisC (PDB ID 2G0D). (E,F) Loss of catalytic activity upon mutation reveals the importance of the His proposed to protonate the enolate during intramolecular nisin cyclase C–S-bond-forming activity as well as intermolecular LanCL-catalyzed C-glutathionylation. The zinc ion binding Cys residues are also essential for LanCL activity.