Figure 6.
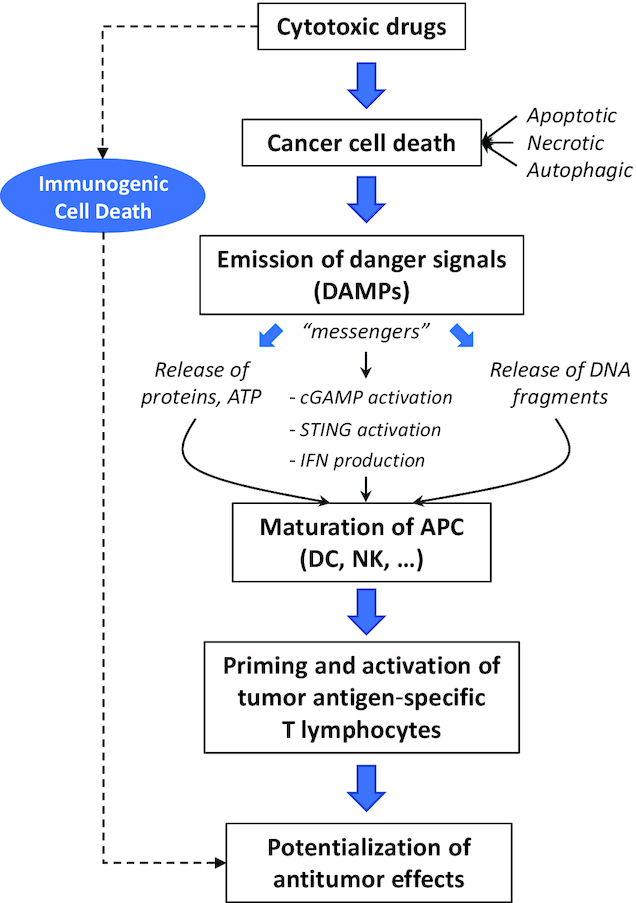
Chemotherapy-induced cancer cell death proceeds via a direct action of cytotoxic drugs on cancer cells (inducing different types of cell death) and via ICD. ICD drives the release of DAMPs that potentiate drug activity. DAMPs stimulate the immune system via the activation of APCs and in particular DCs functionally maturated by NK cells. A variety of DAMPs have been identified (calreticulin, HMGB1, HSP70, ATP and others) depending on the drug mechanism of action (155). DAMP messengers, notably the released cytosolic DNA fragments issued from tumor cells, are sensed via cGAS that activates STING and then induces transcription of type I interferon genes. Activation of the cGAS/STING pathway also promotes transcription of different chemokines (such as CXCL10 and CCL5) that stimulate CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocyte migration in tumor environment, to trigger the antitumor immune response. As such, ICD reinforces the antitumor action of the cytotoxic drugs.
