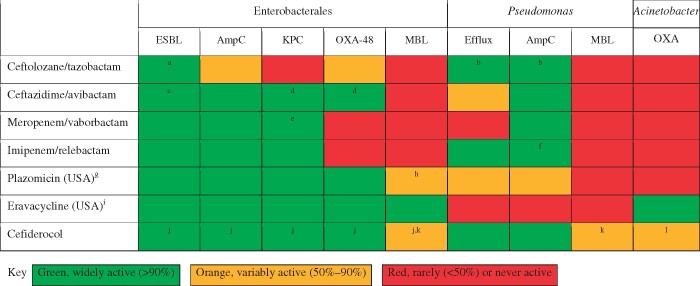
Figure 4.
Activity of recently licensed (USA and EU/UK) agents against problem groups of Gram-negative bacteria. Green, widely active (>90%); orange, variably active (50%–90%); red, rarely (<50%) or never active. aTrial evidence of efficacy.128bIn-use evidence of clinical activity against P. aeruginosa likely, based on phenotypes, to have these mechanisms.129cTrial evidence of efficacy.130dIn-use evidence of efficacy and of better outcomes than colistin combinations.131,132eTrial evidence of better outcomes than colistin combinations.133fTrial evidence of activity against imipenem-resistant P. aeruginosa, likely to have owed their phenotypes to combination of loss of porin OprD and expression of AmpC.134gLicensing application withdrawn in EU. hMany isolates with NDM carbapenemases co-produce ArmA or RmtB 16S rRNA methyltransferases, conferring broad aminoglycoside resistance including plazomicin.135iGood in vitro activity against carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales, but trial failures in cUTI.136jTrial evidence of activity.137kMICs raised for isolates with NDM carbapenemase compared with those for isolates with other carbapenemases; the proportion of these that count as resistant will depend on the breakpoints used.138lIn vitro activity, but excess mortality in CREDIBLE-CR study compared with colistin combinations, associated with Acinetobacter baumannii, suggesting the need for caution.139