Figure 2.
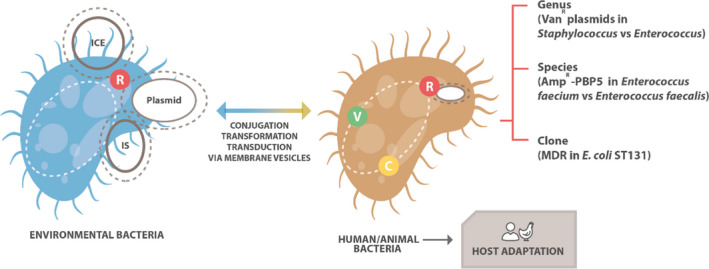
- Antimicrobial resistance genes (R) can be mobilised from an environmental microorganism by different mobile genetic elements (MGEs) (e.g. ICE‐integrative conjugative element; IS‐insertion sequence; plasmid) and transferred through conjugation, transduction, transformation or via membrane vesicles to another bacterial cell. Bacterial virulence (V) and host colonisation features (C) are also important factors for emergence and success of horizontally transferred AMR. Genus, species or clone specificities present in the food‐producing environment may favour the acquisition and maintenance of certain MGE‐encoding ARG. This transfer can also occur in the opposite direction: human and animal bacteria acting as donors of MGE carrying ARGs to environmental bacteria
