Figure 12.
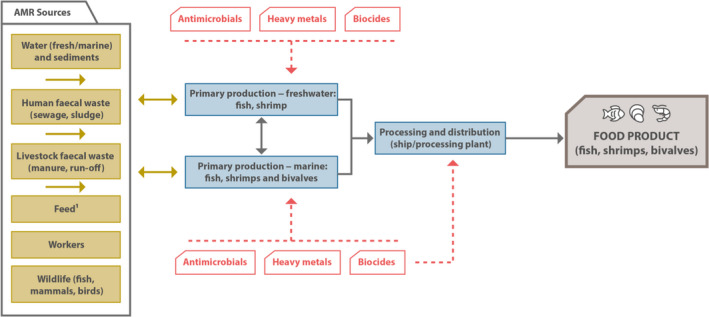
- (1): Only for fish and shrimps, not for bivalves.Potential sources of AMR (resistant bacteria, both human pathogenic, zoonotic, commensal or environmentally associated and/or resistance genes) for the food production environment are shown as dark gold boxes and transmission routes as dark gold arrows. AMR can either be introduced from these sources into the food chain, or AMR can also flow from the food production chain to these sources. Black arrows depict the flow of AMR along the food production chain (blue boxes). Subcategories of the production chains are shown as folders. Red arrows depict the usage of antimicrobial agents and biocides and the presence of heavy metals in food production systems and its effect on AMR (selection of AMR). Workers and visitors signify people with access to the production environment, for either professional or other reasons. Wildlife includes all animals with access to the production chain (such as birds, larger mammals) but excludes pests typically associated with food production. Definitions of terms used are given in the glossary.
