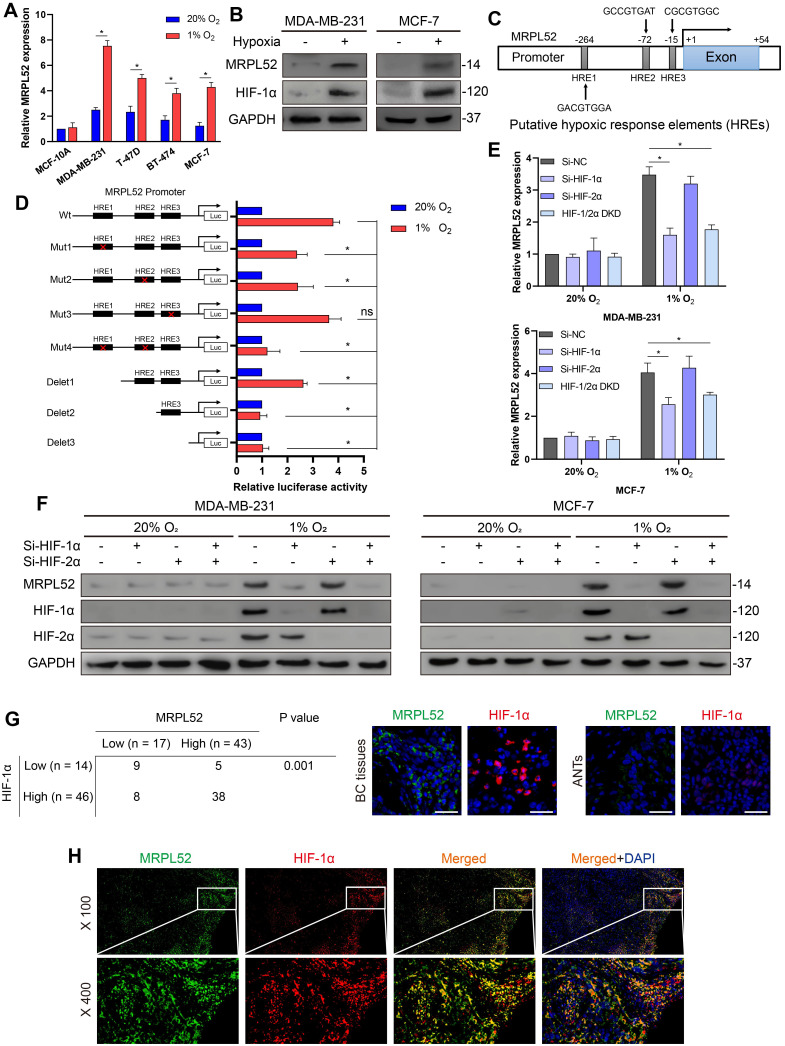
Figure 3.
MRPL52 is transcriptionally activated by HIF-1 in response to hypoxia. (A) RT-qPCR analysis of MRPL52 mRNA levels in 4 BC cell lines and 1 normal breast epithelial cell line exposed to 20% or 1% O2 (mean ± SD, n = 4). *P < 0.05. (B) WB analysis of MRPL52 and HIF-1α in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cell lines exposed to 20% or 1% O2. (C) The JASPAR website was used to predict the potential hypoxic response elements (HREs) in the promoter of MRPL52. (D) Luciferase activities of MRPL52 promoter with the wild type and the mutated HREs in MDA-MB-231 cells exposed to 20% or 1% O2 were determined using a dual-luciferase reporter assay (mean ± SD, n = 3). *P < 0.05. Wt, wild type; Mut, mutant type; Delet, serial deletion; HREs, hypoxic response elements; Luc, luciferase reporter plasmid. (E) RT-qPCR and (F) WB assays were performed to analyze MRPL52 expression level in BC cell under normoxia or hypoxia (mean ± SD, n = 4). *P < 0.05. (G) Left panel, expression of MRPL52 and HIF-1α in 60 BC patients detected by tissue IF. Statistical analysis was carried out by Pearson's χ2 test. Right panel, the representative IF images of MRPL52 (green) and HIF-1α (red) expression in human BC tissues and matched ANTs. Scale bars, 25µm. (H) Representative IF images of MRPL52 (green) and HIF-1α (red) in human BC tissues. Yellow color in the merged image represents the co-localization of MRPL52 and HIF-1α.