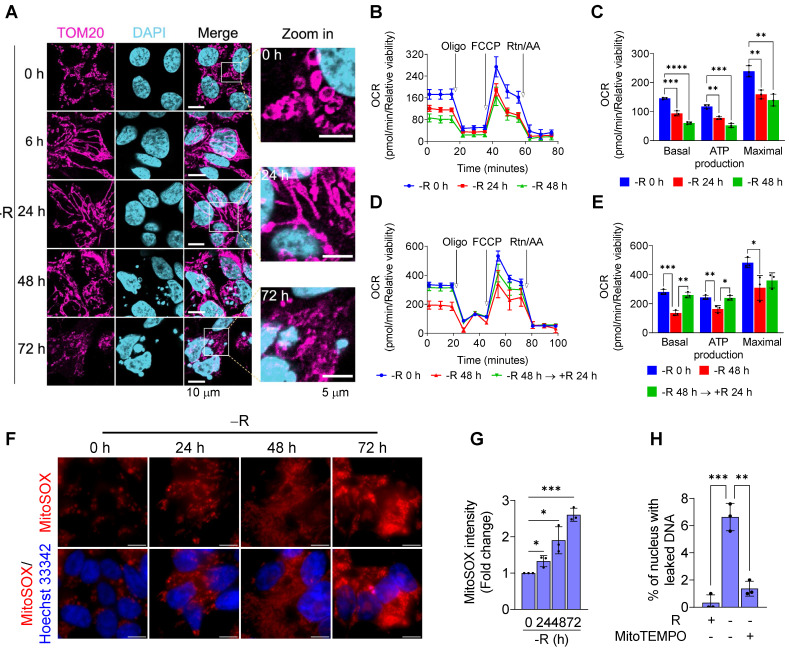
Figure 4.
Arginine starvation altered mitochondrial dynamics and induced mitochondrial dysfunction. (A) Mitochondrial dynamics was visualized by immunostaining of the mitochondrial outer membrane protein, TOM20. (B) Oxygen consumption rate of arginine-deprived CWR22Rv1 cells. (C) Basal respiration, ATP production and maximal respiration in CWR22Rv1 after arginine starvation. (n = 3, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001). (D) CWR22Rv1 cells were deprived for 48 h, followed by reintroducing arginine for another 24 h. Oxygen consumption rate was determined by Seahorse assay. (E) Basal respiration, ATP production and maximal respiration in CWR22Rv1 after arginine reintroduction. (n = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001) (F) Live images of mitochondrial ROS probed with MitoSOX. Scale bars, 10 μm. (G) Mitochondrial ROS was probed by MitoSOX, and fluorescent intensity was quantified. (n = 3, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001) (H) MitoTEMPO was employed to scavenge mitochondrial ROS, and chromatin leakage was quantified by cell counting. (n = 3, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001)