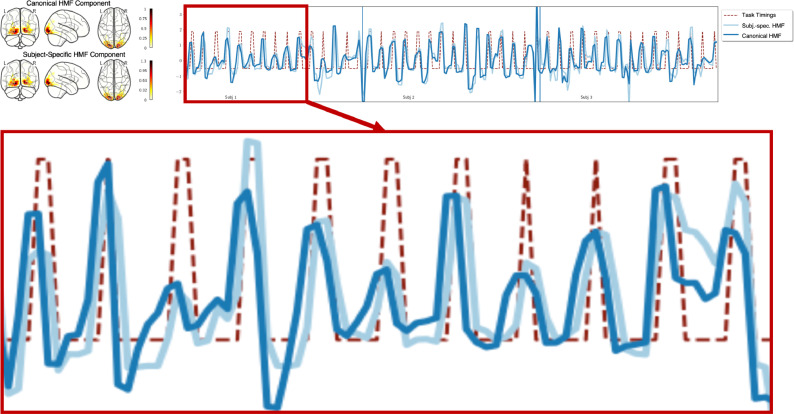
Fig. 10.
The neural activation time courses and spatial maps of the most correlated canonical and subject-specific HMF mode in motor task session one. The enlarged view of neural activation time courses showed that there is a small delay between the neural activation time course of canonical and subject-specific HMF. The canonical HRF takes a longer time to peak than the subject-specific HRF of subject 1 depicted in Fig. The neural activation time course of the corresponding HMF mode with canonical HRF therefore peaks earlier than the neural activation time course of the HMF mode with subject-specific HRF. Ultimately, the subject-specific HRF resulted in a better alignment with task timings (red dashed line) compared to the canonical HRF.