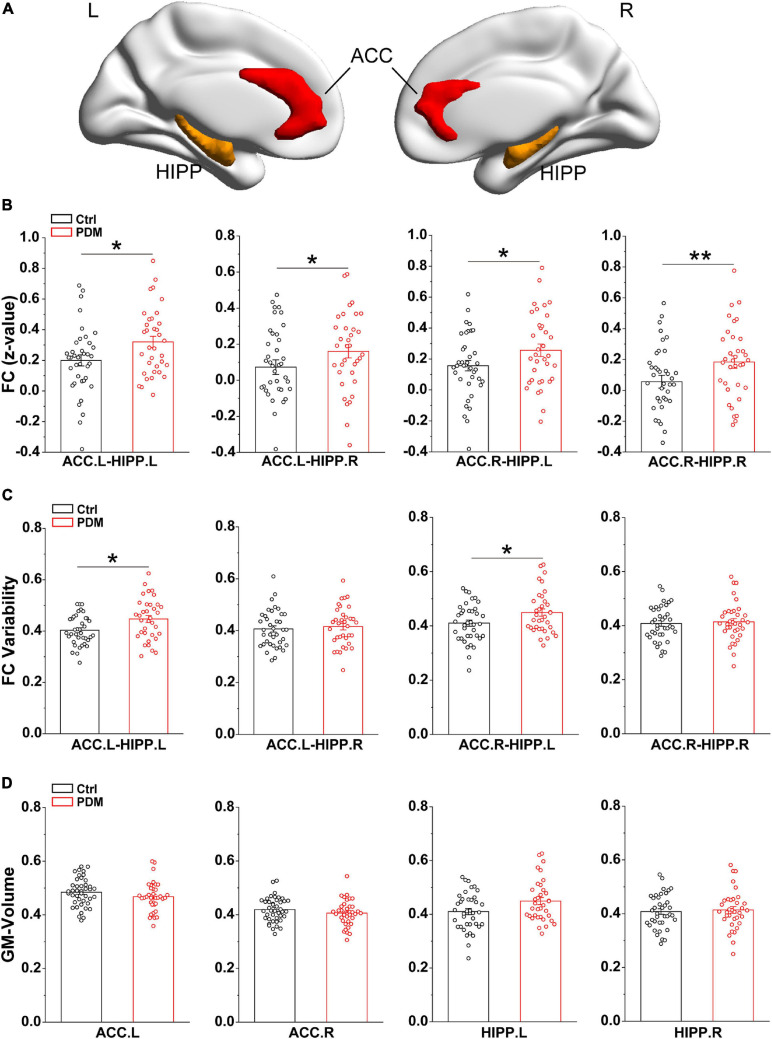
FIGURE 1.
Greater static FC and FC variability between ACC and HIPP, with unchanged GM volumes, in PDM females. (A) Three-dimensional brain view of the ICBM152 MNI depicting the location of the bilateral ACC (red) and HIPP (yellow) based on the Anatomical Automatic Labeling (AAL) atlas. (B) In the static FC, PDM subjects exhibited increased FC between ACC.L-HIPP.L, ACC.L-HIPP.R, ACC.R-HIPP.L, and ACC.R-HIPP.R. (C) The PDM group exhibited significantly greater FC variability between ACC.L-HIPP.L and ACC.R-HIPP.L than controls. (D) The GM volume of both ACC and HIPP did not change significantly in PDM females compared to controls (p > 0.05). L, left hemisphere; R, right hemisphere. Error bars = ± 1 SE. n = 35 (38) and 38 (42) for PDM and control females in the static FC, FC variability (GM volume) analysis, respectively. Non-parametric permutation test with days of menstrual cycle as regressor for static FC, FC variability and GM volume. ∗p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.