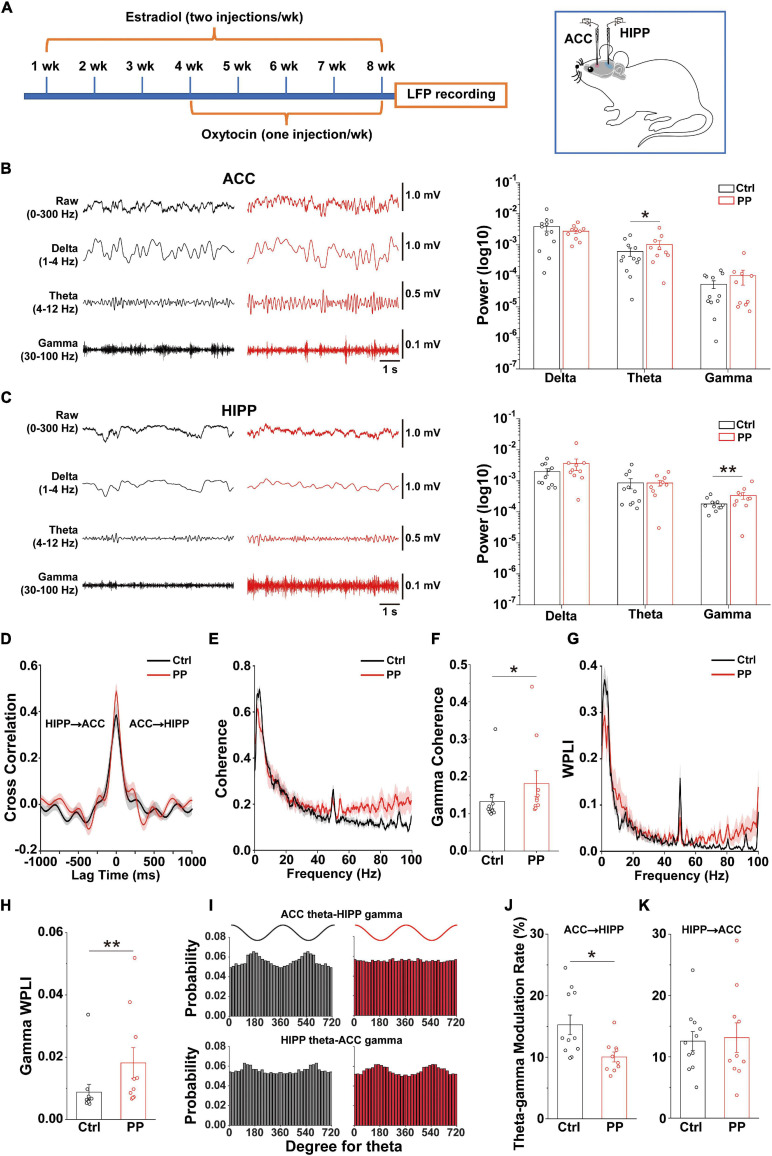
FIGURE 5.
Altered oscillations and connectivity in ACC and HIPP of model rats. (A) Schematic diagram showing the timeline of model rat’s generation and dual channel in vivo LFP recordings in the left hemisphere. Starting from week 4, oxytocin was IP injected 24 h after injection of estradiol. The last dose of oxytocin was injected on day 57 and LFPs were recorded on days 58 and 59. (B) Representative traces of extracellular LFPs, as well as filtered delta, theta and gamma oscillations in the ACC of both groups (left). ACC oscillatory power in the theta band increases significantly in model compared to control rats, while delta and gamma oscillations remain identical between the two groups (z = –0.281, p = 0.779 for delta; z = –2.209, p = 0.027 for theta; z = 0.114, p = 0.909 for gamma; Mann–Whitney test). (C) Representative traces of extracellular LFPs, as well as filtered delta, theta and gamma oscillations in the HIPP of both groups (left). HIPP of model rats show significantly increased oscillatory power in the gamma band, while delta and theta oscillations remain identical between the two groups (z = –1.45, p = 0.147 for delta; z = –0.88, p = 0.379 for theta; z = –2.723, p = 0.006 for gamma; Mann–Whitney test). (D) The simultaneous LFP signals between ACC and HIPP have approximately symmetrical cross-correlation values at positive (ACC leading) and negative (HIPP leading) time lags in model and control animals, suggesting bidirectional communication between these two brain areas. (E) Averaged coherence curve between LFPs in ACC and HIPP. Notably, model rat differs significantly from control rats in the gamma band. (F) Gamma coherence between ACC and HIPP in model rats is significantly higher than that of controls (z = –2.289, p = 0.022; Mann–Whitney test). (G) Averaged WPLI curve between LFPs recorded in ACC and HIPP. (H) Gamma WPLI between ACC and HIPP is significantly higher in model rats (z = –2.711, p = 0.0067; Mann–Whitney test). (I) Probability distribution of cross-frequency theta-gamma coupling in both directions. (J,K) Quantification shows significantly reduced modulatory effect of ACC theta on HIPP gamma activity (p = 0.034), while modulation by HIPP theta of ACC gamma remains unchanged (p = 0.818; two-way ANOVA). Values represent mean ± SEM. n = 10–12; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.