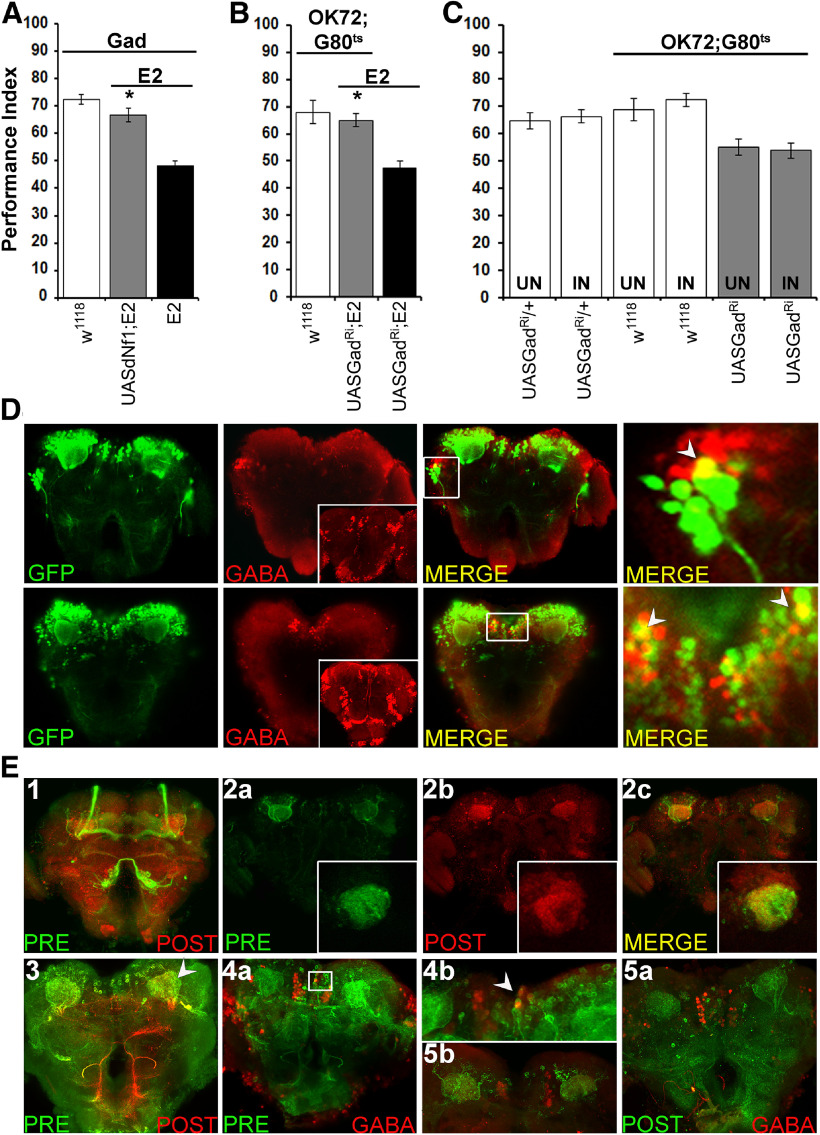
Figure 3.
Olfactory associative learning requires dNf1 in GABAergic OK72-marked neurons. A–C, Performance was assessed within 3 min after conditioning in control (white bars), mutant (black bars), and experimental (gray bars) animals. The genotypes are indicated below each bar, representing the mean ± SEM. *Statistically significant difference of the experimental from mutant flies. G80ts indicates the ubiquitously expressed temperature-sensitive Gal4 repressor Tub-Gal80ts. A, Expression of the UAS-Nf1 transgene within GABAergic neurons restores normal learning to dNf1E2 nulls. B, Adult-specific Gad abrogation (UASGadRi) within OK72 neurons reverses the learning deficit of dNf1E2 homozygotes to levels not significantly different from that of controls. C, RNAi-mediated abrogation of Gad (UASGadRi) in OK72 neurons of adult WT flies does not alter learning at the restrictive (18°C, UN) or the permissive temperature (30°C, IN), respectively (gray bars). White bars represent the control genotypes, raised at both temperatures. D, All images are at 40× magnification. Size bar indicates relative size. Anti-GFP staining (green), anti-GABA staining (red), and merging of the two (yellow) in representative optical sections from fly brains where GFP expression is driven by OK72-Gal4. The insets in the GABA panels are maximum projections to demonstrate ample penetration of the anti-GABA antibody not obvious in the optical sections used for colocalization. Colocalization of GFP and GABA immunofluorescence is detected laterally (top) and the SMP (bottom). Right panels (both top and bottom), Magnifications of the respective marked boxes, showing colocalization in single cells. E, In flies bearing the trans-Tango components, driving ligand and myrGFP expression under OK72-Gal4 (green) results in HA-mtdTomato expression in postsynaptic MB dendrites (red). Anterior (E1) and posterior (E3) view of maximum projections of presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons under OK72Gal4-driven TANGO. E2a–E2c, Representative optical sections of presynaptic (OK72; green) and postsynaptic (red) neurons at the dendritic level, where yellow represents their interaction. Insets, Higher magnification of confocal images from different brains at the level of MB dendrites. E4a, Posterior view maximum projection of OK72 presynaptic neurons (green) and GABA-positive neurons (red). White box represents the area magnified (80×) in E4b with the white arrow indicating colocalization. E5a, Posterior view maximum projection of postsynaptic to OK72-marked neurons (green) and GABAergic ones (red), clearly showing no colocalization. E5b, Area in the posterior of a different brain than in E5a verifying independently the lack of GABA (red) colocalization with postsynaptic to OK72-marked neurons (green).