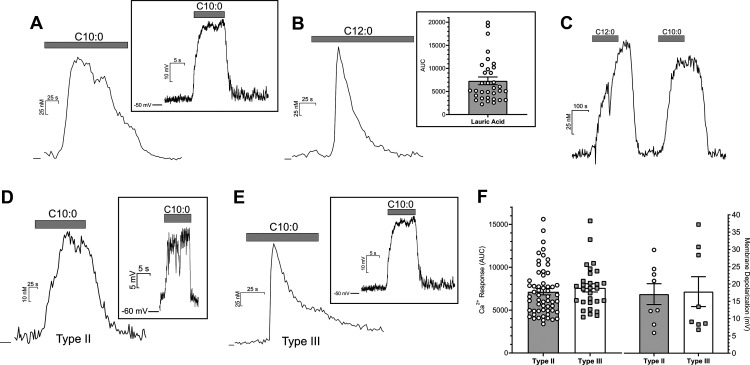
Figure 3.
Taste cell responses induced by MCFAs. Bath application of capric acid (C10:0; 100 μm, A) and lauric acid (C12:0; 100 μm, B) elicited intracellular calcium rises in mouse taste cells. B, Inset, The range of calcium responses seen in taste cells to lauric acid. Focal application of capric acid (200 μm) induced a membrane depolarization in taste cells (A, inset). Lauric acid and capric acid induced similar calcium responses in the same taste cells (C). Cells were held at zero current level to measure membrane potential in current-clamp mode. MCFAs also induced robust calcium increases and membrane depolarization (insets) in GFP-positive taste cells from both GFP-PLCβ2 (Type II cells; D) and GFP-GAD67 mice (Type III cells; E). F, both Type II and Type III cells show similar calcium response magnitudes and degree of membrane depolarization in response to a mixture of capric acid (100 μm) and lauric acid (100 μm). Data presented show only those cells that met the criterion for a responsive cell.