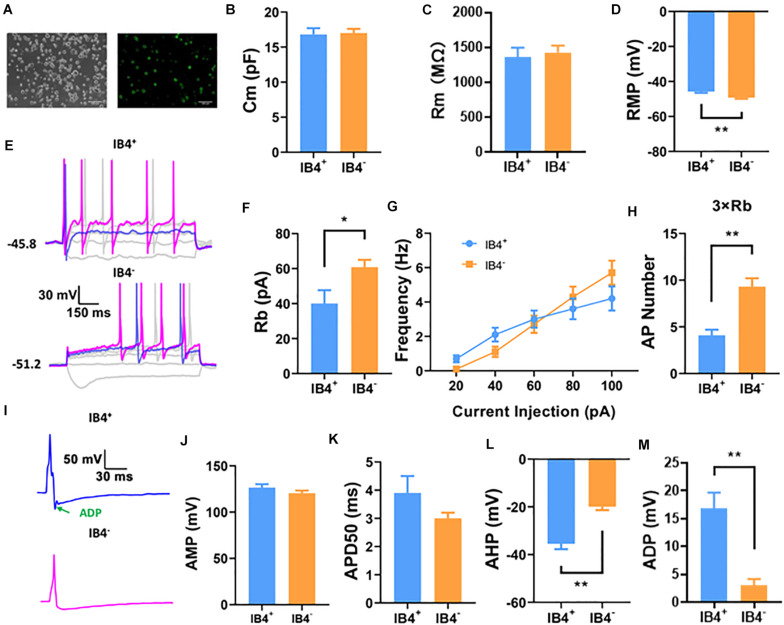
FIGURE 1.
Comparison of passive and active properties of IB4+ and IB4– subpopulations of small DRG neurons in mouse. IB4+ and IB4– subpopulations of small DRG neurons (<25 μm), separated by the staining of IB4-FITC (A). Small DRG neurons were recorded in current-clamp mode using a perforated configuration of whole-cell patch clamping. To avoid the confounding effects of IB4 staining on the forming of Giga-seal for patch clamp recording and potentially on the electrophysiological properties of DRG neurons, the DRG neurons were stained immediately after recording. Representative recordings using a long (1,000 ms) or short (5 ms) step current protocol were shown in (E,I), respectively. Passive properties including membrane capacitance [Cm, (B)], membrane resistance [Rm, (C)], resting membrane potential [RMP,(D)], and active properties including rheobase [Rb, (F)], frequency (G), number at 3x rheobase (H), amplitude [AMP, (J)], half duration [APD50, (K)], afterhyperpolarization [AHP, (L)], and afterdepolarization [ADP, (I,M)] of action potentials were compared between IB4+ and IB4– neurons. n = 17–38 for each groups (see detailed numbers for each group in results). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; Student’s t-test.